Batteries: AA, C and D – Understanding the Difference
Batteries are an important part of our daily lives. From remote controls to large flashlights, they power a variety of devices and keep us connected in this fast-paced world. However, not all batteries are created equal. Have you ever wondered why some devices require AA batteries and others require C or D batteries? What is the difference between them and how does this affect the performance of your device?
In this article, we will compare the size, weight, voltage and other parameters of AA, C and D batteries in detail. In addition, we’ll discuss practical applications, advantages, and trade-offs to help you make an informed decision the next time you choose a battery for your device.
All About AA Rechargeable Batteries
C Batteries Explained: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding D Cell Batteries: A Quick Guide
Part I: Size – How Battery Size Affects Power and Performance
One of the most obvious differences between AA, C and D batteries is their size. Size plays a critical role in determining a battery’s energy storage, longevity, and compatibility with various devices.
- AA Battery Size: AA batteries are the smallest of the three, measuring approximately 50.5 mm in length and 14.5 mm in diameter. Their compact size makes them ideal for devices that don’t require a lot of power but are used frequently, such as remote controls, wall clocks and handheld game consoles.
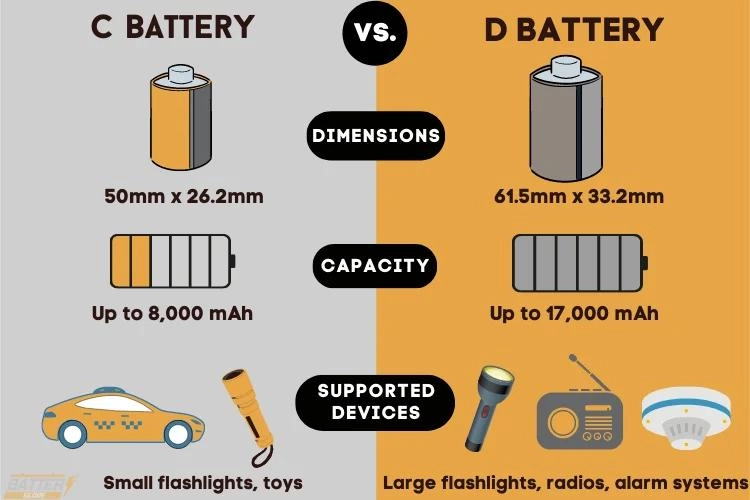
- C Battery Specifications: C batteries are larger in size, measuring 50 millimeters in length and 26.2 millimeters in diameter. These batteries are typically used in devices that require more power than AA batteries but do not need the high capacity of D batteries. Common applications include medium-sized flashlights or specific toys.
- D Cell Specifications: D cells are the largest of the three, measuring 61.5 mm in length and 34.2 mm in diameter. They are best suited for high power consuming devices such as large flashlights, portable radios, and certain medical devices where consistent, long-lasting power is critical.
The larger the size of the battery, the greater its ability to store energy, which is why larger batteries like D cells are ideal for devices that require long periods of time and don’t need to be replaced as often.
Part 2: Weight – Why heavier batteries last longer
Another important factor to consider is the weight of the battery. Generally speaking, the heavier the battery, the more energy it stores and the longer it lasts.
- AA Battery Weight: AA alkaline batteries weigh about 23 grams. Because of their light weight, they are great for small portable devices such as wireless mice, TV remotes, or digital cameras. However, the light weight also means they don’t last as long as larger batteries in high-powered devices.
- C Battery Weight: Weighing about 65 grams, C batteries offer a good balance of size and power. These batteries are typically used in devices such as radios and medium-sized flashlights, which require moderate power and therefore more durable batteries.
- D Battery Weight: D batteries are the heaviest of the three, weighing about 140 grams. While they may seem bulky, the added weight provides significant benefits. These batteries are designed to power devices for long periods of time and are ideal for high power consumption applications such as handheld stereos and large flashlights that need to be powered for hours on end.
When selecting these battery types, consider the trade-off between weight and longevity. While lighter batteries are easier to carry, heavier batteries provide longer-lasting power, especially in high-drain devices.
Part 3: Voltage – Same Voltage, Different Capacity
The alkaline versions of AA, C and D batteries all utilize a standard voltage of 1.5 volts. However, the real difference is in the amount of energy they can store and release over time.
- AA Batteries: standard AA batteries have a voltage of 1.5 volts, making them ideal for small household appliances. However, their limited capacity compared to C and D batteries means that they need to be replaced more frequently in high-powered devices. For devices that require a more permanent power source, it may be helpful to consider using solar cell storage.
Part I: Introduction to Battery Types
When it comes to household batteries, there are three common sizes that come to mind: the AA, C, and D. While they may look similar in shape, each has a different purpose and is suitable for different devices. In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between AA, C, and D batteries, focusing on their sizes, capacities, and applications so you can make the best choice for your needs.
Part 2: Size Differences
The main difference between AA, C and D batteries is size. While they all have a standard voltage of 1.5 volts, their energy storage capacities are quite different, which can affect their performance in different devices.
- AA batteries: These are the smallest of the three, measuring approximately 50 mm in length and 14 mm in diameter.AA batteries are typically used in devices that consume a small amount of power, such as remote controls, clocks, and toys. They are compact and easy to use, but store less energy than larger batteries.
- Type C batteries: Type C batteries are slightly larger in size, measuring about 50 millimeters in length and 26 millimeters in diameter. They have a higher energy capacity than AA batteries, making them ideal for medium-drain devices that require a more stable power source, such as radios and toys.
- D cell: This is the largest of the three, measuring approximately 61 mm in length and 34 mm in diameter. This battery has the largest power storage capacity and is suitable for high power consumption devices such as flashlights, portable radios and large toys.
The size of each battery determines the amount of energy it can store, which in turn directly affects its performance and duration in the device.
Part 3: Voltage Consistency of Different Battery Types
All AA, C and D batteries have a standard voltage of 1.5 volts. This stable voltage ensures compatibility with a wide range of equipment. However, although the voltage is the same, the capacity (the amount of energy that can be stored) varies, thus affecting the runtime of the device.
- AA Batteries: Suitable for low-drain devices, AA batteries provide enough voltage to power everyday items such as TV remotes, wireless keyboards and wall clocks. However, they may need to be replaced more frequently in high power consumption devices.
- C batteries: C batteries hold more power and therefore last longer than AA batteries. They are ideal for medium-drain devices such as flashlights and portable radios that require long battery life.
- D batteries: D batteries are preferred for devices that require a lot of power for a long period of time. They are perfect for high power consumption devices such as large flashlights, power tools and industrial equipment.
These battery types have a stable voltage that ensures their versatility, but the varying capacities determine how long each battery will last.
Part IV: Battery Capacity – Energy Storage and Lifespan
Battery capacity is measured in milliampere hours (mAh) and indicates how long a battery can last before needing to be replaced. The larger the battery and the higher the capacity, the longer it will power your device.
- AA Batteries: AA batteries typically have a capacity of 1,800 to 2,850 mAh. While sufficient for low-drain devices such as remote controls, they drain quickly for high-drain devices such as digital cameras or portable fans.
- C batteries: C batteries have a capacity of between 6,000 and 8,000 mAh and last longer than AA batteries. They are ideal for medium-drain devices such as radios and toys, providing consistent performance for long periods of time.
- D batteries: D batteries have the largest capacity, ranging from 12,000 to 18,000 mAh. They are designed for high-drain devices and are ideal for large flashlights and heavy-duty equipment that require stable power for long periods of time.
The higher the capacity, the longer the battery life, making D batteries the preferred choice for devices that require constant, extended power.
Part 5: Uniform Cylindrical Design
Although AA, C, and D batteries come in different sizes, they all have a cylindrical shape. This standard design allows them to fit into a variety of battery boxes. However, the larger the battery, the more energy it stores, which can affect its performance in a variety of applications.
Part 6: Rechargeable Options
All three types of batteries are available in rechargeable versions, usually using nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) chemistry. Not only are rechargeable batteries more environmentally friendly, but they also offer significant cost savings over time.
- AA Rechargeable Batteries: AA rechargeable batteries are the most common batteries and can be recharged up to 1000 times. They are ideal for frequently used devices such as wireless controllers and digital cameras, and are a low-cost alternative to single-use batteries.
- C Rechargeable Batteries: These rechargeable batteries have a higher capacity than AA rechargeable batteries and are ideal for products that consume a moderate amount of power, such as radios, toys and flashlights. These batteries have a longer rechargeable life and are an excellent choice for the environment.
- D-Type Rechargeable Batteries: Designed for high power consumption devices, D-Type rechargeable batteries provide a more sustainable and cost-effective power source for larger devices such as heavy-duty flashlights and power tools.
Rechargeable batteries are an excellent choice for users who regularly use batteries to power their equipment, helping to reduce waste and save money in the long run.
Part 7: Lifespan – How long each battery lasts
The lifespan of a battery depends on how long the device is used before the battery needs to be replaced. Factors such as the power requirements of the device and the capacity of the batteries have a significant impact on battery life.
- AA Batteries: In devices with low power consumption (such as clocks and remote controls), AA batteries can last for months. However, in devices that consume a lot of power (such as digital cameras), AA batteries may only last a few hours or days before they need to be replaced.
- C batteries: C batteries are more durable than AA batteries, especially in products with moderate power consumption, such as radios or children’s toys. Depending on the device, they can last for weeks or even months before needing to be replaced.
- D-Type Batteries: D-Type batteries excel in devices that use a lot of power, providing long-lasting power for up to several months for devices such as large flashlights and portable radios. Their long lifespan makes them ideal for devices that require constant, high power output for extended periods of time.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between AA, C and D batteries in terms of size, capacity and lifespan will help you choose the right battery for your device. Whether you need fast, low power consumption or long-lasting, high power consumption, these battery types offer a variety of solutions to meet your needs.
Part VIII: Chemistry – The Different Components That Power Your Device
The chemistry of a battery plays a critical role in its performance, longevity, and environmental impact.AA, C, and D batteries typically have three main chemistries: alkaline, lithium, and nickel-metal hydride (rechargeable).
Alkaline Batteries:
Alkaline batteries are the most common type of battery and provide reliable performance for most everyday devices. They are disposable and, while not the most environmentally friendly option, are easy to use.
Lithium batteries:
Lithium batteries are lightweight and perform well in extreme temperatures. They’re perfect for outdoor use or high-tech products that require a constant supply of power, independent of the environment.
NiMH Batteries:
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are the preferred choice for rechargeable power supplies. Available in AA, C and D sizes, they offer stable performance and can be used continuously and recharged multiple times.
Part IX: Applications
Each battery type is suitable for a specific application based on its size, capacity and weight.
AA batteries:
AA batteries are typically used in devices with low power consumption, such as remote controls, clocks, and wireless mice. They are perfect for small, everyday household appliances that don’t need to consume a lot of power.
C-type batteries:
C-type batteries are typically used in devices such as flashlights, radios and certain toys. They offer a good balance of size and power and are ideal for medium power consumption devices.
D Batteries:
D batteries are best suited for high-capacity power-hungry devices such as large flashlights, portable speakers and industrial equipment. They provide long-lasting power for heavy-duty applications.
Part 10: Are AA, C and D batteries interchangeable?
A common question is whether AA, C and D batteries are interchangeable. While it may seem convenient to replace one type of battery with another, the differences in size and capacity often make it impractical to do so without using an adapter or making significant changes to performance. The reasons are as follows:
Physical size matters:
The main reason these batteries are often not interchangeable is because of their different sizes. the different diameters and lengths of AA, C, and D batteries mean that they won’t fit into a device designed for other battery sizes. For example, trying to fit a D battery into a slot designed for AA batteries is impossible due to the size mismatch.
Compatibility adapters:
Battery adapters can be used to fit small batteries, such as AA, into devices with large batteries, such as D. The adapters can be used to fit small batteries, such as AA, into devices with large batteries. However, this has its limitations. Although the voltage is the same (1.5V), the capacity of the smaller battery is much lower, resulting in the device draining power more quickly. For example, replacing a D battery with an AA battery will work for a short period of time, but the difference in capacity is so great that it will need to be replaced frequently.
Power and device compatibility:
Even if smaller batteries can fit into a larger battery compartment, the power requirements of the device must be considered. Devices that require C or D batteries usually need the higher capacity and longer run times provided by these larger batteries. Replacing them with smaller batteries, such as AA batteries, may cause the device to degrade in performance or run out of power quickly. For example, replacing D-cell batteries in a large flashlight with AA batteries may result in dimmer light and the need for frequent battery replacements.
While adapters can provide some interchangeability, for optimal performance and longer-lasting power, we always recommend that you use the battery specifications and types specified by the manufacturer.
Part 11: How to choose the right battery for your device
Choosing the right battery depends on a variety of factors, including the power requirements of your device, how often it’s used, and whether portability is important. Let’s explore the key factors.
Choosing the right battery: AA, C or D?
When deciding whether to use AA, C or D batteries, it is important to consider the specific power requirements of your equipment. Each battery size has its own unique advantages, depending on the needs of the equipment and your priorities.
1. Equipment Power Needs
The first step in choosing the correct battery size is to evaluate the power needs of your device. For low-power devices such as TV remotes or wireless mice, AA batteries are usually sufficient. If you have a medium-drain device such as a portable radio or toy, a C battery is a better choice because it has a higher capacity. For high power consumption devices such as large flashlights, portable speakers, or medical equipment, D batteries are the best choice because they provide long-lasting power for extended use.
2. Battery Capacity
Capacity plays a crucial role when it comes to battery life; D batteries have the largest capacity and are ideal for devices that need to run for long periods of time without needing to be recharged, C batteries provide a good balance, and AA batteries, although smaller in size, are ideal for devices that don’t need to be used for long periods of time and don’t have high demands.
3. Frequency of use
For devices that are used frequently, rechargeable batteries are a more economical and environmentally friendly option. Whether it’s a game controller, digital camera or radio, rechargeable AA, C or D batteries can help you save money over the long term, reduce battery waste and are a more sustainable option.
4. Portability
If you need something lightweight and easy to carry, AA batteries are the way to go. They’re great for portable electronics like wireless microphones, clocks, and small toys. However, for larger, power-hungry devices that don’t need to be moved around as often, C or D batteries can provide the longer runtimes needed for continuous operation.
5. Cost Considerations
While C and D batteries tend to be more expensive than AA batteries, they last longer, making them more economical in the long run for devices that consume a lot of power. For devices that consume less power, AA batteries are affordable and widely available for everyday use.
6. Environmental Impact
If sustainability is important to you, consider using rechargeable NiMH batteries. Available in AA, C, and D sizes, these batteries can be reused hundreds of times, greatly reducing battery waste. While they have a higher initial cost, their long-term benefits far outweigh the cost in terms of savings and environmental impact.
To summarize
Picking the right battery among AA, C and D sizes may seem simple, but knowing the details of each can have a significant impact on the performance and longevity of your device.AA batteries are ideal for small, low-power devices, while C and D batteries provide more power for medium- to high-drain devices.
By considering the size, weight, voltage and capacity of each battery, you can ensure that your device runs efficiently. Keep in mind that while adapters allow for some flexibility, using the battery type recommended by the manufacturer is always the best option for optimal performance.
Whether you’re powering a remote control, flashlight or portable speaker, knowing the difference between AA, C and D batteries will help you make the right choice. If you use batteries on a regular basis, buying rechargeable batteries can save you money and be kinder to the environment.
For more information on battery efficiency, read our guide to lithium batteries, which highlights the advantages of lithium batteries over conventional batteries.
A Comprehensive Guide to Safely Cleaning Leaking Battery Leads
This guide provides a step-by-step look at the possible risks, safety precautions, and proper cleaning methods when dealing with leaking battery leads.
Portable battery chargers vs. mobile power: what’s the difference?
A portable battery charger is any device that can be charged on the move, whereas a mobile power supply is used to store energy in a battery in order to charge a device without an external power source.
The Ultimate Guide to Using Lithium-Ion Starter Power
Lithium-ion starter power is an essential tool for car emergencies. This guide will cover its usage, safety tips, maintenance guidelines, and explain why it’s a smart investment for your car.
What is a portable battery charger?
A portable battery charger is a convenient and useful device that can power your devices while you’re on the go. This guide outlines the definition, materials, and operation of a portable battery charger so you can easily understand it.
How to choose the best battery pack for your needs: capacity, performance and more
Choosing the right battery pack is key to ensuring reliability and performance. This guide covers important aspects such as capacity, safety and other important factors to help you make the best choice.