A Comprehensive Guide to Battery Types: Alkaline, Zinc Carbon and Lithium Batteries
Batteries play a vital role in our daily lives, powering a wide range of devices from household appliances to electric vehicles. Understanding the differences between alkaline, zinc carbon and lithium batteries is essential to choosing the type of battery that meets your needs. This guide will provide an in-depth look at the features, benefits, and ideal uses for each type of battery.
Part 1: What are Alkaline Batteries?
Alkaline batteries are one of the most commonly used batteries in household devices. They produce electricity through a chemical reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide and use an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide.
Key Features:
- Voltage: alkaline batteries typically have a voltage of 1.5 volts per cell, making them suitable for a wide range of devices.
- Shelf life: If properly stored, these batteries can last up to 10 years with stable and reliable performance.
- Capacity: Alkaline batteries usually have a higher capacity than carbon zinc batteries, ranging from 1,000 to 2,800 mAh depending on the battery size and brand.
Benefits of Alkaline Batteries:
- Longer life: In power-hungry devices such as digital cameras and game controllers, alkaline batteries last much longer than zinc carbon batteries.
- Widely available: Alkaline batteries are easily available at most retail stores and online platforms.
- Widely used: in a variety of devices including toys, flashlights, and portable electronics.
Part 2: What are Carbon Zinc Batteries?
Carbon-zinc batteries are one of the oldest battery technologies still in use today. They consist of a zinc anode and a carbon rod cathode and contain an acidic electrolyte that produces the chemical reaction needed to generate electricity.
Key Features:
- Voltage: like alkaline batteries, zinc carbon batteries have a voltage of 1.5 volts.
- Shelf life: Compared to alkaline batteries, zinc carbon batteries have a shorter shelf life, typically lasting 3 to 5 years under optimal storage conditions.
- Capacity: Zinc carbon batteries typically have a lower capacity than alkaline batteries, ranging from 400 to 1,000 mAh.
Advantages of Zinc Carbon Batteries:
- Cost Effective: Carbon zinc batteries are typically more affordable than alkaline and lithium batteries, making them attractive to budget-conscious consumers.
- Lightweight design: Carbon zinc batteries are lightweight and easy to handle.
- Ideal for low-drain devices: Zinc carbon batteries perform well in low-drain devices such as clocks and remote controls, which do not require high power output.
Part III: What are lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries are known for their high energy density and long shelf life. They use lithium as the anode material and are categorized into primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable).
Key Features:
- Voltage: Lithium batteries typically provide a high voltage of about 3 volts per cell, thus providing efficient power for more demanding devices.
- Shelf life: If properly stored, these batteries can last up to 10 years or more, making them ideal for emergency equipment or gadgets that are not used often.
- Capacity: of the three batteries discussed in this article, lithium batteries have the largest capacity, with standard sizes (such as the CR2032 or AA variants) typically having a capacity of more than 2,500 mAh.
Advantages of lithium batteries:
- High energy density: they are smaller but have more energy than alkaline or zinc carbon batteries.
- Longer shelf life: Lithium batteries have a low self-discharge rate, so they can hold a charge longer and last longer than alkaline and zinc carbon batteries.
- Rechargeable Options: Many lithium batteries can be recharged multiple times without a noticeable drop in performance, making them more cost-effective over the long term for power-hungry applications such as digital cameras or smartphones.
Part IV: Performance Comparison: Alkaline, Zinc Carbon and Lithium Batteries
When choosing between the above battery types, consider factors such as voltage, capacity, shelf life and cost effectiveness. Each battery type has its own unique benefits for different needs and uses. Whether you are looking for a reliable and durable battery for your equipment or an affordable battery for a low-drain device, understanding these key differences will help you make an informed decision.
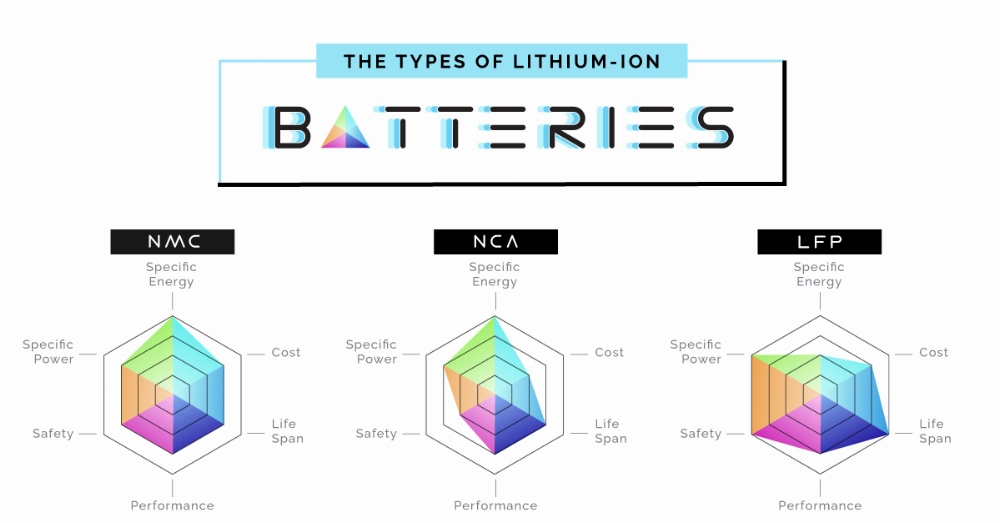
For those interested in the efficiency of lithium-based technology, exploring the benefits of lithium iron phosphate batteries may be a wise next step.
KHZH
Battery Performance Comparison: Alkaline, Zinc Carbon, and Lithium Batteries
Understanding the differences in battery performance is critical to making the right choice for your device. Below is a detailed analysis based on a variety of factors:
Voltage and Energy Output:
- Alkaline and zinc carbon batteries have a voltage of 1.5 volts/cell, while lithium batteries have a higher voltage of about 3 volts/cell. This higher voltage allows lithium batteries to effectively power more demanding devices.
Capacity:
The capacity of each type of battery varies greatly:
- Alkaline batteries: typically between 1000 and 2800 mAh.
- Zinc carbon batteries: capacities range from 400 to 1000 mAh.
- Lithium: starts at around 2500 mAh and can go higher depending on size and design.
Self-discharge rate:
- Lithium batteries have the lowest self-discharge rate, losing only about 1% of their charge per year.
- Alkaline batteries lose about 10% of their charge per year if left unused.
- Carbon-zinc batteries have the highest self-discharge rate, losing about 20% per year.
Function Comparison
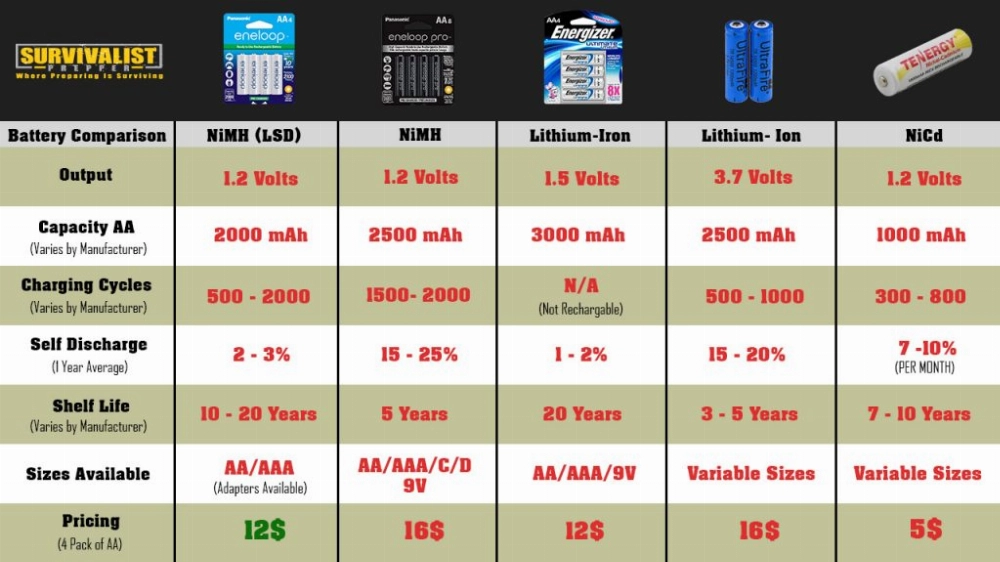
| Function | Alkaline | Zinc Carbon | Lithium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.5V | 3V |
| Shelf life | Up to 10 years | 3 to 5 years | Up to 10 years |
| Capacity | 1,000 – 2,800 mAh | 400 – 1,000 mAh | 2500+ mAh |
| Self-discharge rate | Approx. 10% per year | Approx. 20% per year | Approx. 1% per year |
| Weight | Medium | Light | Light |
| Rechargeable | No | No | Yes (in some cases) |
Section 5: Ideal Applications for Each Battery
Understanding the ideal use cases for each type of battery will help you make an informed decision:
- Alkaline batteries: Best for toys, flashlights, and portable electronics.
- Zinc Carbon Batteries: Ideal for clocks, remote controls, and low-drain devices.
- Lithium batteries: Ideal for digital cameras, smart phones, and high-performance electronic devices.
Part VI: Environmental Impact of Various Battery Types
The environmental impact of batteries is a growing concern, and sustainability should always be a consideration:
- Alkaline batteries: They are less harmful than other batteries if disposed of properly, but the materials they contain can still be harmful to the environment if not recycled.
- Zinc Carbon Batteries: They are often considered less environmentally friendly due to their low recycling rate and heavy metal content.
- Lithium Batteries: Although they have a high recycling potential, improper disposal may be harmful to the environment due to the activity of lithium.
Part 7: Cost Comparison: Which Battery is More Affordable?
When evaluating cost, consider the initial price and overall life of the battery:
- Alkaline Batteries: Moderately priced, but have a long service life, making them more cost effective in the long run.
- Carbon-zinc batteries: Typically, these batteries have the lowest initial cost, but are replaced more frequently.
- Lithium Batteries: Although they have a higher initial cost, they are typically more economical in power-hungry applications due to their long life and reusability.
Part 8: Safety Precautions for All Types of Batteries
Safety is critical when handling batteries:
- Alkaline batteries: usually safe, but may leak if damaged or improperly stored.
- Carbon-zinc batteries: are not prone to leakage, but may rust if not used properly.
- Lithium batteries: are safe under normal conditions, but can lead to dangers such as overheating or explosion if damaged or improperly charged.
Part 9: Choosing the right battery for your needs
Choosing the right battery depends on your specific requirements:
- Alkaline batteries: best suited for everyday household items with moderate power requirements.
- Zinc carbon batteries: Cost-effective solution for use in low-drain devices.
- Lithium: Often the best choice for high-performance gadgets that require reliable power for long periods of time.
Part 10: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main differences between alkaline and lithium batteries?
The main differences are voltage and energy density. Lithium batteries typically have a higher voltage (3V) and energy density compared to alkaline batteries.
Understanding the Different Types of Batteries: Carbon-Zinc, Alkaline, and Lithium
Can I use zinc carbon batteries instead of alkaline batteries?
While zinc carbon batteries can replace alkaline batteries, performance may vary. Carbon-zinc batteries are less effective in high-drain devices, while alkaline batteries are superior because carbon-zinc batteries have a shorter lifespan with frequent use.
Are lithium batteries rechargeable?
Some lithium batteries are indeed rechargeable. However, it is important to check the specifications before use, as not all lithium batteries are rechargeable.
Which type of battery lasts the longest?
Lithium batteries usually last longer than other types of batteries such as alkaline and zinc carbon batteries because they have a higher energy density and a lower self-discharge rate.
What should I do with these batteries?
Battery disposal should always comply with local regulations. Recycling programs are available for zinc carbon, alkaline and lithium batteries, but regulations may vary by region. Always ensure that you dispose of your batteries responsibly.
Related Article:
-
How to Safely Clean the Leads of a Leaking Battery: A Step-by-Step Guide
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of safety tips, risks and proper cleaning methods for handling leaking batteries. -
Portable Battery Charger vs. Mobile Power: What’s the Difference?
A portable battery charger is a device that charges other devices, while a mobile power supply is used to store energy to charge devices when power is unavailable. -
The Ultimate Guide to Lithium-Ion Starters
Learn how to use, maintain and fully utilize your lithium-ion starter power supply in an emergency. It’s a smart investment for your car! -
What is a portable battery charger?
Portable battery chargers power your devices while you’re on the go. Understanding how they work, what they’re made of, and why they’re essential for your technology needs. -
How to choose the best battery pack for your needs: capacity, performance and more
Choosing the right battery pack is critical to reliability. Learn about capacity, performance and the key factors that will help you choose the best option.