When evaluating and comparing different batteries, especially in areas such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics, watt-hours (Wh) and amp-hours (Ah) are two commonly used terms. Understanding the relationship between these units is essential for accurately assessing and selecting batteries. This guide will explore definitions, calculations, and practical examples to help you easily convert between watt-hours and amp-hours.
Part 1: What is a Watt-Hour?
Watt-hour (Wh) is a unit that represents the energy capacity of a device or battery. It indicates the total amount of energy a device can provide over a specific period. Watt-hours are calculated by multiplying voltage (V), current (I, measured in amperes), and time (h, measured in hours). Simply put, a watt-hour is the energy consumed or produced by a one-watt device operating for one hour.
How to Calculate Watt-Hours
To calculate the watt-hours of a device or battery, you need to know the voltage and current. You also need to know the time the current flows for. The calculation formula is as follows:
Battery Capacity and Efficiency: Key Considerations
When selecting a battery, it’s crucial to understand the key factors that influence its performance to ensure it meets your energy needs. Here’s a breakdown of essential concepts:
Efficiency and Run Time
- Watt-hours (Wh) represent the total amount of energy a battery can store and provide. A higher watt-hour rating indicates a larger energy reserve, allowing the device to run for a longer duration.
- Amp-hours (Ah) represent the battery’s ability to sustain a specific current over a period of time. A higher amp-hour rating means it can power your device for longer.
- To select the right battery, consider both watt-hours and amp-hours to match your device’s power requirements. For high-power devices, opt for batteries with larger capacities, while smaller capacities may suffice for low-power devices.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the conversion between watt-hours and amp-hours is essential for evaluating energy capacity and comparing battery performance. Understanding these calculations will help you make more informed battery choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many watt-hours are there in 100Ah?
To calculate watt-hours, multiply amp-hours by voltage. For example, if the voltage is 12 volts, the calculation for 100Ah is as follows:
100Ah * 12V = 1200 watt-hours.
How do you calculate power rating (in watts)?
The power rating in watts is determined by multiplying the voltage in volts by the current in amperes. The formula is:
P (Power in Watts) = V (Voltage in Volts) * I (Current in Amperes).
How do you calculate watt-hours from watts?
While the term ‘watts per hour’ is not a standard unit, you can calculate watt-hours by multiplying power in watts by time in hours. For example, if a device operates at 100 watts for 2 hours, the energy consumed is:
100 Watts * 2 Hours = 200 watt-hours.
What is the difference between watt-hours and watts per hour?
Watt-hours (Wh) measure the energy consumed or stored over time, while watts per hour (W/h) is not a standard unit. It’s more accurate to refer to the *rate of change of power over time*, which is *sometimes incorrectly referred to* as ‘watts per hour’.
Is a 4.0 Ah battery better than a 2.0 Ah battery?
It depends on the application. A 4.0 Ah battery has twice the energy storage capacity of a 2.0 Ah battery. Therefore, if your device requires more energy, the 4.0 Ah battery would be a better choice.
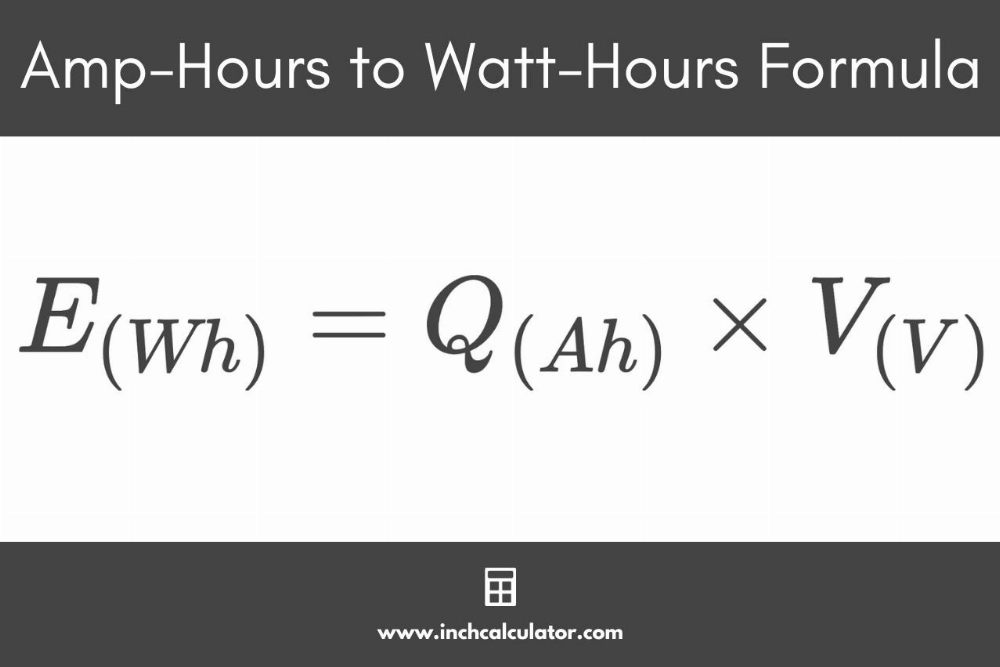
High-Nickel vs. Low-Nickel Ternary Lithium Batteries: What’s the Difference?
Ternary lithium batteries are categorized by their nickel content. High-nickel batteries offer higher energy but can have reduced safety. Low-nickel batteries, on the other hand, provide better safety but have lower energy density. In summary, high-nickel batteries prioritize energy at the expense of safety, while low-nickel batteries prioritize safety at the expense of energy.
At KHZH, we’re dedicated to helping you understand the nuances of battery technology so you can make informed decisions for your projects and applications. Whether you prioritize performance or safety, choosing the optimal battery for your needs is crucial.







