Gel Battery vs. Lithium Battery: Which Should You Choose?
When deciding between a gel battery and a lithium battery, it’s important to understand their unique features, advantages, and potential drawbacks. Whether you’re just starting to explore the world of batteries or you’re a seasoned expert, this comparison will help you determine which battery type is best suited for your needs.
Part 1: What is a Gel Battery?
Gel batteries, also known as gel cell batteries, are a type of rechargeable battery that uses a gel electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. The gel electrolyte is a thick, jelly-like substance that immobilizes the electrolyte, preventing spills and leaks.
Advantages of Gel Batteries:
- Maintenance-Free: Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries, gel batteries are sealed and require no maintenance, making them exceptionally convenient.
- Spill-Proof: The gel electrolyte ensures that the battery is completely spill-proof, making it safer to handle and suitable for sensitive environments.
- Deep-cycle Performance: Gel batteries are designed for frequent deep discharge and recharge cycles, making them ideal for applications such as renewable energy systems.
Disadvantages of Gel Batteries:
- Overcharge Sensitivity: Gel batteries are susceptible to damage from overcharging, which can shorten their lifespan and reduce performance if not properly managed.
- Temperature Sensitivity: These batteries may exhibit reduced performance in extremely hot or cold temperatures compared to other battery types.
- Higher Initial Cost: Gel batteries generally have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional lead-acid batteries; however, their maintenance-free operation can offset this expense over the long term.
Common Applications:
- Solar Power Systems: Gel batteries are frequently used in off-grid solar power systems to reliably store energy for residential and commercial use.
- Recreational Vehicles (RVs): RV owners often prefer gel batteries for their excellent deep cycle performance and maintenance-free operation, providing power for lighting, appliances, and electronics.
- Marine: Gel batteries’ spill-proof design and resistance to vibration make them ideal for marine applications, powering onboard electronics, navigation systems, and more.
Part 2: What is a Lithium Battery?
Lithium batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions to store and release electrical energy. Lithium batteries have become increasingly popular due to their high energy density and superior performance.
Advantages of Lithium Batteries:
- High Energy Density: Lithium batteries can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package compared to other rechargeable batteries.
- Long Lifespan: These batteries typically have a longer lifespan than other types of batteries, making them suitable for long-term use in various applications.
- Fast Charging: Lithium batteries charge faster than most other rechargeable batteries, resulting in quicker turnaround times.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: These batteries have a low self-discharge rate, allowing them to hold their charge for extended periods when not in use.
- Versatility: Lithium batteries come in different sizes and formats, making them versatile for a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to electric vehicles.
Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries:
- Cost: The initial cost of lithium batteries is often higher than other battery types, but prices have been steadily decreasing as the technology matures.
- Safety Concerns: While generally safe, lithium batteries can overheat or even experience thermal runaway (a dangerous condition that *may* lead to combustion) if damaged or mishandled.
Common Applications:
- Consumer Electronics: Lithium batteries are widely used in devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and digital cameras due to their long-lasting performance and high energy density.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Lithium batteries power most electric vehicles, providing longer driving ranges, faster charging times, and lighter weight.
KHZH provides detailed information on the pros and cons of lithium-ion batteries, to help you make an informed decision regarding your energy storage needs.
Understanding the Applications and Advantages of Lithium and Gel Batteries
Part 1: Applications of Lithium Batteries
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Lithium batteries are widely used in electric vehicles, providing the necessary driving energy. Their high energy density and fast charging capabilities make them the preferred choice for electric vehicle manufacturers.
Renewable Energy Storage
Lithium batteries play a crucial role in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power. They store excess energy generated during peak production periods for use during low-production times or at night.
Aerospace
Lithium batteries are essential in aerospace applications, including spacecraft, satellites, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs, drones).
Medical Devices
Lithium batteries are commonly found in medical devices such as pacemakers, hearing aids, and portable medical equipment. Their long cycle life and reliability make them ideal for these applications.
Part 2: Gel vs. Lithium Batteries
1. Technology:
- Gel Batteries: These are lead-acid batteries with the electrolyte suspended in a gel.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries use lithium as one of the active materials and have higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
2. Energy Density:
- Gel Batteries: Typically, gel batteries have lower energy density than lithium batteries, meaning they store less energy per unit of volume or weight.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries are known for their high energy density, allowing them to store more energy in a smaller and lighter package.
3. Lifespan:
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries generally have a shorter lifespan than lithium batteries, especially in applications that require frequent deep discharges.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries offer a longer lifespan, making them more suitable for long-term use in various applications.
4. Maintenance:
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries are maintenance-free, requiring no water addition or electrolyte checks, which makes them convenient for users.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries also require minimal maintenance, but may need occasional monitoring to ensure optimal performance and safety.
5. Charging:
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries may require longer charging times, especially after deep discharges.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries can be charged quickly, providing rapid power replenishment.
6. Cost:
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries often have a lower initial cost compared to lithium batteries, making them a more affordable option for some users.
- Lithium Batteries: While lithium batteries typically have a higher upfront cost, their longer lifespan and higher energy density may offer better long-term value.
7. Safety:
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries are considered safe to use, with a low risk of leakage or thermal runaway.
- Lithium Batteries: While offering higher energy density, lithium batteries can pose safety risks if mishandled, overcharged, overheated, or physically damaged.
Part 3: Key Considerations When Choosing Between Gel and Lithium Batteries
Energy Density
Lithium batteries have a higher energy density than gel batteries, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller and lighter form. If you need high energy output while minimizing weight and size, lithium batteries are the preferred choice.
Weight and Size Constraints
For applications that require lightweight and compact batteries, lithium batteries are more suitable. Due to their higher energy density, they are generally smaller and lighter. In contrast, gel batteries tend to be bulkier and heavier, making them unsuitable for situations where weight or space is severely restricted.
Cycle Life
Consider the expected usage pattern of the battery. Lithium batteries have a longer cycle life compared to gel batteries, meaning they can handle more charge and discharge cycles before experiencing performance degradation. This makes lithium batteries a better long-term investment, especially in high-demand applications.
Battery Comparison: Lithium vs. Gel Batteries
Performance
In terms of performance, lithium batteries stand out with their higher energy density and longer lifespan. They are better suited for applications that require high power and long runtime. On the other hand, gel batteries are more susceptible to performance degradation over time, especially when subjected to heavy cycling. Lithium batteries are superior when frequent cycling or long-term durability is required.
Charging Speed
Lithium batteries typically offer faster charging capabilities compared to gel batteries. If rapid charging and minimal downtime are desired, lithium batteries are preferable.
Maintenance
Gel batteries are generally maintenance-free, meaning they don’t require electrolyte replenishment or specific maintenance tasks. In contrast, while lithium batteries also have very low maintenance needs, they may require occasional monitoring and cell balancing to ensure optimal performance.
Environmental Considerations
Consider the environment in which the battery will be used. Gel batteries are quite durable, perform well in a variety of temperatures, and can withstand extreme conditions.
Cost
Gel batteries have a lower upfront cost compared to lithium batteries. However, it’s crucial to assess the long-term cost-effectiveness. While lithium batteries have a higher initial cost, they offer better long-term cost-effectiveness due to their longer lifespan and higher energy density.
Safety Considerations
Safety is another key factor to consider. Both gel and lithium batteries are generally safe if handled properly. However, lithium batteries have a slightly higher risk of thermal runaway if damaged, exposed to extreme conditions, or mishandled.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which battery type is superior: lithium or gel?
The choice between lithium and gel batteries depends on your specific needs. Lithium batteries offer superior energy density and a longer lifespan but come with a higher upfront cost. Gel batteries are more affordable and require less maintenance but have lower energy density and lifespan.
How many years do gel batteries last?
The lifespan of a gel battery can vary depending on usage, charge/discharge cycles, and maintenance. Typically, a well-maintained gel battery can last for 3 to 8 years.
What can damage a gel battery?
Several factors can contribute to the degradation and eventual failure of a gel battery, including deep discharge, overcharging, exposure to extreme temperatures, physical damage, and sulfation resulting from chronic undercharging.
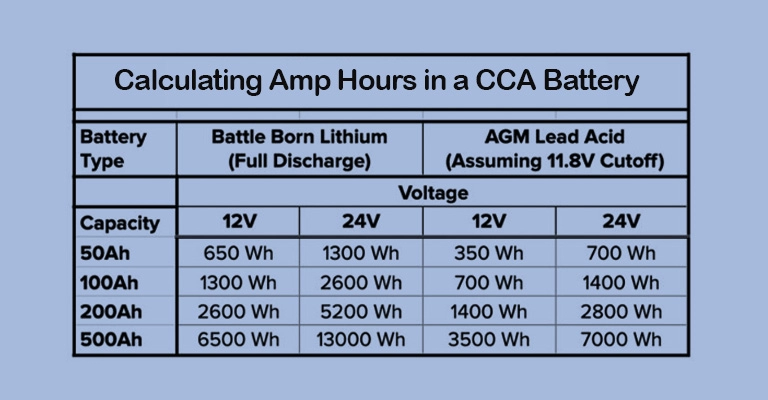
What size inverter do I need for a 200Ah lithium battery?
The size of the inverter you need for a 200Ah lithium battery depends on the power requirements of the appliances you plan to run. To determine the appropriate inverter wattage, estimate the total wattage of the devices you intend to use simultaneously, or the peak wattage if devices have surge requirements, and then choose an inverter with a continuous output wattage slightly higher than the total wattage.
Related Tags
- KHZH
- Lithium Battery Content Creation
Portable Battery Charger vs. Power Bank: What’s the Difference?
A portable battery charger is any device that allows for portable charging, while a power bank specifically stores energy in a battery to charge devices when a power source isn’t available.
The Ultimate Guide to Lithium-Ion Jump Starters
Lithium-ion jump starters are essential tools for automotive emergencies. This guide will walk you through how to use them, the safety tips, and the maintenance. It will also explain why it is a wise investment for all car owners. To learn more about how lithium-ion batteries work in various applications, check out our Lithium-Ion Battery 3.7V vs 7.4V Differences Explained article.
What is a Portable Battery Charger?
A portable battery charger is a convenient solution for keeping your devices charged while you’re on the move. This guide explores its definition, key materials, and how it works. It offers a clear and easy-to-understand explanation.