A common question when it comes to batteries is: Are 1.5V batteries equivalent to 9V or 12V batteries? Understanding battery voltages is essential for ensuring compatibility and optimizing performance in various devices. This article explores the key differences between these battery voltages, their applications, and common questions to improve your understanding.
Part 1: Understanding Battery Voltage
Battery voltage plays a fundamental role in determining a battery’s performance in different applications. It represents the potential difference between two points in a circuit, essentially indicating how much energy is available to push electrons through the system.
What Does Voltage Mean?
Voltage can be compared to the “pressure” that drives electric current through a circuit. Higher voltage means there is more potential energy available to do work, while lower voltage indicates less energy.
Why Are Different Voltages Needed?
Different devices require a specific amount of energy to operate effectively. Here are some common applications:
- 1.5V Batteries: Suitable for low-power devices like remote controls, flashlights, and toys.
- 9V Batteries: Commonly used in smoke detectors, guitar effects pedals, and medical devices that need more power.
- 12V Batteries: Typically found in automotive applications, power tools, and larger electronic devices requiring substantial energy output.

Part 2: Battery Types
Understanding the different types of batteries helps clarify their performance, lifespan, and suitability for various applications.
Common Battery Types
Alkaline Batteries
- Pros: Affordable, widely available, and have a long shelf life.
- Cons: Limited capacity for high-drain devices; performance decreases under heavy loads.
Lithium Batteries
- Pros: Higher energy density, longer lifespan, and perform better in extreme temperatures.
- Cons: More expensive than alkaline batteries; can be hazardous if punctured or mishandled.
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Pros: High capacity, cost-effective per watt-hour, and reliable, especially for automotive use.
- Cons: Heavy, bulky, require maintenance, and can leak if damaged.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Pros: Rechargeable, higher capacity than alkaline batteries, and less susceptible to the memory effect than Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) batteries.
- Cons: More expensive than alkaline batteries; higher self-discharge rate compared to lithium batteries.
Battery Chemistry
Battery chemistry significantly influences voltage and performance characteristics:
- Alkaline: Provides a stable voltage but has limited capacity for high-drain devices.
- Lithium: High energy density and long lifespan but higher cost.
- Lead-acid: Lead-acid batteries are suitable for high-capacity applications but are heavy and require significant maintenance.
Part 3: Comparing 1.5V, 9V, and 12V Batteries
Understanding the differences in voltage levels helps in selecting the appropriate battery for specific applications.
Voltage Levels and Applications
- 1.5V Batteries: Best suited for low-power devices like flashlights, remote controls, and toys. They provide enough energy for simple tasks without overloading the circuit.
- 9V Batteries: Designed for medium-power devices like smoke detectors, guitar effects pedals, and medical instruments. They offer more energy than 1.5V batteries while maintaining a compact size.
- 12V Batteries: Commonly used in automotive applications, power tools, and large electronic products. These batteries provide robust power for high-drain devices like electric vehicles and heavy machinery.
Performance Characteristics
Voltage differences translate into different performance attributes:
- Capacity: While all three types store energy, the capacity (measured in mAh or Ah) varies. Generally, higher voltage batteries tend to have larger capacities.
- Discharge Rate: Higher voltage batteries can handle larger loads, making them suitable for more demanding applications.
- Size and Weight: Smaller devices tend to use 1.5V or 9V batteries, while 12V batteries are typically larger and heavier due to their higher power output.
Understanding battery voltages, chemistries, and performance characteristics enables users to make more informed choices for different applications.
markdown
# Understanding Battery Voltage, Compatibility, and Environmental Impact
Battery Capacity and Discharge Rates
Capacity Comparison
Batteries come in various voltages and capacities, affecting their performance and applications. For example:
- AA Alkaline Batteries (1.5V): Typically have a capacity of 2000-3000mAh. (mAh stands for milliampere-hour)
- Standard 9V Batteries: Often contain 500-600mAh due to their compact size.
- Lead-Acid Batteries (12V): Range from a few amp-hours to hundreds, depending on their application. (Ah stands for ampere-hour)
Discharge Rates
Batteries of different voltages exhibit different discharge characteristics:
- 1.5V Batteries may struggle under high-load conditions, such as running a motor.
- 12V Lead-Acid Batteries can handle significant loads without performance degradation.
Compatibility Issues
Using the incorrect battery voltage can lead to serious problems:
Risks of Voltage Mismatch
- Device Damage: Overvoltage can cause overheating or failure.
- Poor Performance: Undervoltage may lead to improper operation.
When is it Acceptable to Substitute Batteries?
Some devices have built-in voltage regulators that can tolerate minor variations. However, always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications before substituting batteries.
Environmental Impact of Batteries
Batteries pose significant environmental concerns, making proper disposal and finding suitable alternatives crucial.
Recycling Batteries
Proper disposal and recycling prevent harmful substances from contaminating soil and water. Many communities offer specialized recycling programs for used batteries.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives
Consider using rechargeable batteries, such as NiMH or Lithium-Ion, which reduce waste and are more cost-effective in the long run.
Importance of Battery Rating Parameters
Battery rating parameters help determine their performance and suitability for specific uses.
Understanding Amp-Hours (Ah)
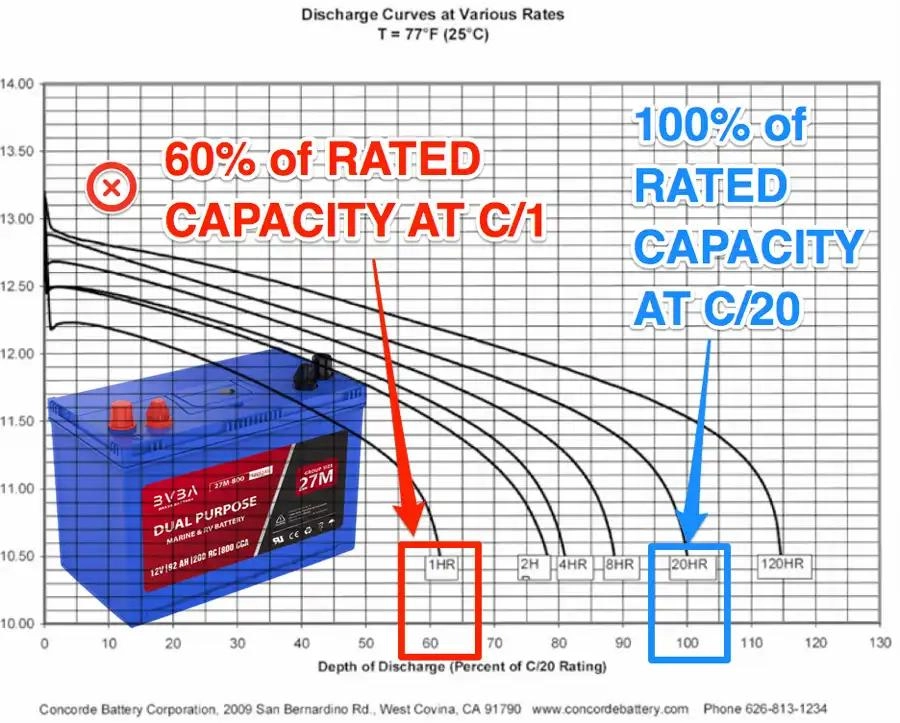
The Ah rating measures how long a battery can deliver a specific current. A higher Ah rating allows for longer operation, especially at lower power consumption levels.
C-Rating
The C-rating specifies how quickly a battery can safely discharge. A higher C-rating is essential for high-drain devices (devices that require a lot of power quickly).