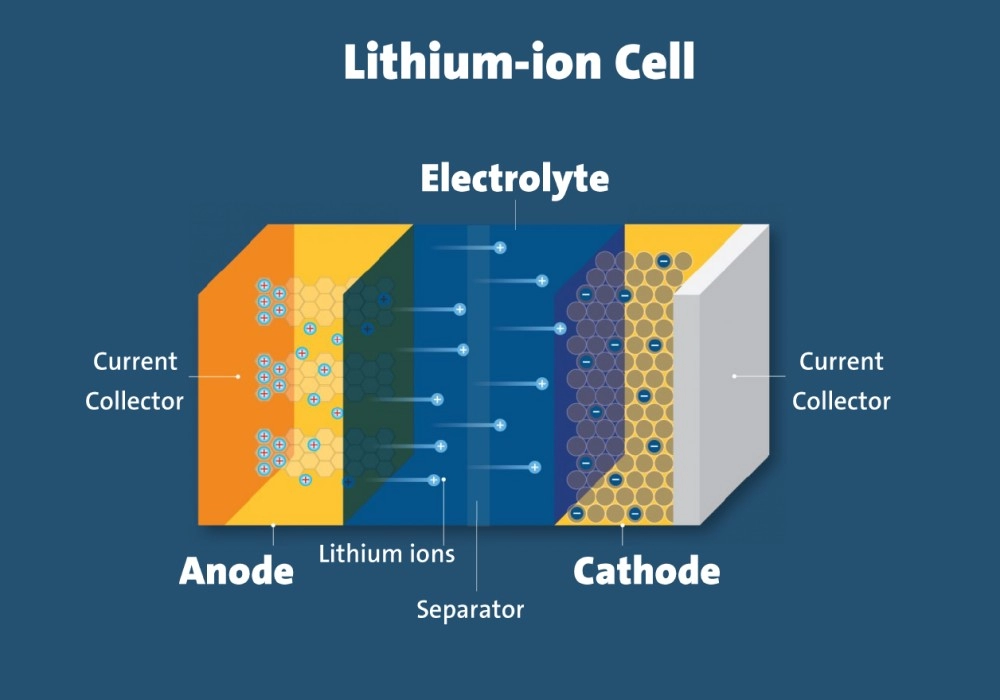
Understanding the Difference Between 3.7V and 7.4V Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become an essential part of modern life, powering devices ranging from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, it’s important to note that not all lithium-ion batteries are the same. One common point of confusion is the difference between 3.7V and 7.4V lithium-ion batteries. In this article, we will explore the details of these two batteries, highlighting their characteristics, applications, and differences. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of which battery is best suited for your needs.
Part 1: Are All Lithium-Ion Batteries the Same Voltage?
Lithium-ion batteries come in a variety of voltages. The voltage of a lithium-ion battery depends on the number of cells it contains and their arrangement (series or parallel). A single lithium-ion cell typically has a nominal voltage of 3.7 V. However, when cells are connected in series, the voltages are additive. For example, two 3.7V cells connected in series will produce a 7.4V battery. This voltage variation allows for different battery configurations to meet the specific power needs of various devices.
In addition to the nominal voltage of a 3.7V lithium-ion battery, there are other important voltage levels to consider:
- Full Charge Voltage: A 3.7V lithium-ion battery, when fully charged, has a voltage of around 4.2V per cell.
- Nominal Voltage Range: The nominal voltage of a 3.7V lithium-ion battery typically ranges between 3.0V (when discharged) and 4.2V (when fully charged).
- Operating Voltage: The operating voltage is the voltage range within which the battery can be safely discharged.
- Cut-off Voltage: The cut-off voltage is the minimum voltage at which a device or charger stops discharging or charging the battery to prevent over-discharge or overcharge. For a 3.7V lithium-ion battery, the cut-off voltage is typically around 3.0V per cell.
These voltage levels play a crucial role in battery management and ensure the safety and longevity of the battery.
Part 2: How to Calculate Series Voltage of 3.7V Li-ion Batteries
To calculate the total voltage of a series-connected lithium-ion battery pack, multiply the nominal voltage of a single 3.7 V cell by the number of cells.
For example, if three 3.7 V lithium-ion cells are connected in series, the total voltage is calculated as follows:
*Total Voltage = 3.7V * 3 = 11.1V*
Conversely, when cells are connected in parallel, the voltage remains constant, while the capacity increases.
Part 3: What Factors Affect the Voltage of Li-ion Batteries?
Several factors can affect the voltage of Li-ion batteries:
- Number of Cells: The more cells connected in series, the higher the voltage.
- State of Charge: A battery’s voltage varies depending on its charge level. A fully charged Li-ion cell can reach 4.2V, while a fully discharged cell can drop to around 3.0V.
- Battery Age: As batteries age, their capacity and voltage may decrease due to repeated charge and discharge cycles.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the voltage and overall performance of batteries. High temperatures may increase the voltage, while low temperatures may decrease it.
Part 4: 3.7V vs 7.4V Li-ion Batteries – What Are the Differences?
1. Voltage
- 3.7V Battery: This is the nominal voltage of a single Li-ion cell. It is a standard voltage for many small electronic devices.
- 7.4V Battery: This is the nominal voltage of two 3.7V cells connected in series. Its higher voltage makes it suitable for devices requiring more power.
2. Capacity
- 3.7V Battery: Typically, a 3.7V battery has a lower capacity than a 7.4V battery since it consists of only one cell. However, it is typically sufficient for the energy needs of small electronic devices.
For more insights into battery types and their applications, check out our Lithium Battery vs Lead Acid Battery Comparison.
Comprehensive Comparison of 3.7V and 7.4V Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in various applications, with 3.7V and 7.4V lithium-ion batteries being two of the most popular choices. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right battery for your device. The following is a detailed analysis of their differences:
1. Voltage and Capacity
- 3.7V Battery: 3.7V batteries are typically single-cell configurations. This provides a nominal voltage of 3.7V, making them suitable for smaller devices requiring moderate power output. While their capacity is generally lower, it’s sufficient for low-power devices.
- 7.4V Battery: 7.4V batteries are essentially two 3.7V batteries connected in series, boosting the voltage to 7.4V. This configuration is ideal for higher-power devices such as laptops, drones, and certain medical devices.
2. Energy Density
- 3.7V Battery: Due to their lower voltage, 3.7V batteries tend to have a lower overall energy density. They are commonly used in low-power devices, making them a frequent choice for small electronics.
- 7.4V Battery: On the other hand, 7.4V batteries offer more energy storage due to their dual-cell configuration. This makes them well-suited for high-power devices like drones and electric vehicles.
3. Size and Weight
- 3.7V Battery: As a single-cell unit, 3.7V batteries are generally smaller and lighter. This makes them ideal for portable devices where size and weight are important considerations.
- 7.4V Battery: 7.4V batteries are larger and heavier because they contain two cells. This accommodates the higher power demands of larger devices.
4. Price
- 3.7V Battery: 3.7V batteries are typically more affordable due to the use of fewer cells and simpler materials. They are an economical choice for small, low-power devices.
- 7.4V Battery: 7.4V batteries tend to be more expensive due to the inclusion of an extra cell and a more complex Battery Management System (BMS).
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 3.7V and 7.4V Li-ion batteries is crucial for selecting the right power source for your specific needs. While 3.7V batteries are compact and cost-effective, making them ideal for smaller devices, 7.4V batteries offer higher capacity and power output, making them suitable for more demanding applications. By evaluating factors like application, size, cost, performance, and safety, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and longevity for your devices.
Related Tags:
- Ufine
- Electronic Engineering Writer
More Articles
How to Safely Clean Leaked Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Guide
This step-by-step guide explains the risks, safety precautions, and proper cleaning methods for handling and cleaning corroded battery terminals.
Portable Battery Charger vs Power Bank: What’s the Difference?
A portable battery charger is a general term for any device that can charge batteries on the go, while a power bank stores energy in a battery, allowing devices to be charged without a power source.
The Ultimate Guide to Using a Lithium-Ion Jump Starter
Lithium-ion jump starters are indispensable tools for automotive emergencies. This guide explores its usage, safety aspects, maintenance requirements, and investment value.
What is a Portable Battery Charger?
Portable battery chargers allow devices to be powered on the go. This guide offers an easy-to-understand explanation of its definition, components, and functionality.
How to Choose the Right Battery Pack for Your Needs: Capacity, Performance, and More
Choosing the right battery pack is essential for ensuring reliability and optimal performance. This guide covers key factors like capacity, safety, and other important considerations to help you choose the best option.