Part 1: What Batteries Do LED Lights Use?
When it comes to powering LED lights, not all batteries are created equal. Let’s take a closer look at the main types of batteries commonly used for LED lighting:
1. Alkaline Batteries

Alkaline batteries are the reliable workhorses of the battery world. They’re ubiquitous, ready to power a wide range of small LED devices. Here’s why they’re so widely used:
- Affordable and easy to find
- Long shelf life when not in use
- No memory effect, so you can use them anytime without worry
However, there are some downsides. Alkaline batteries are not rechargeable, leading to increased waste and higher long-term operating costs. Plus, their performance can decrease in extreme temperatures.
2. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries

Lithium-ion batteries are the powerhouses of LED lighting. They’re perfect for high-end rechargeable LED lights, offering benefits such as:
- High energy density – higher power density in a compact form factor.
- Long lifespan – can be recharged hundreds of times
- Low self-discharge rate when not in use
However, they have a higher initial cost and require special charging circuits to prevent overheating. To learn more about these batteries, check out our Lithium-Ion Battery Guide.
3. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
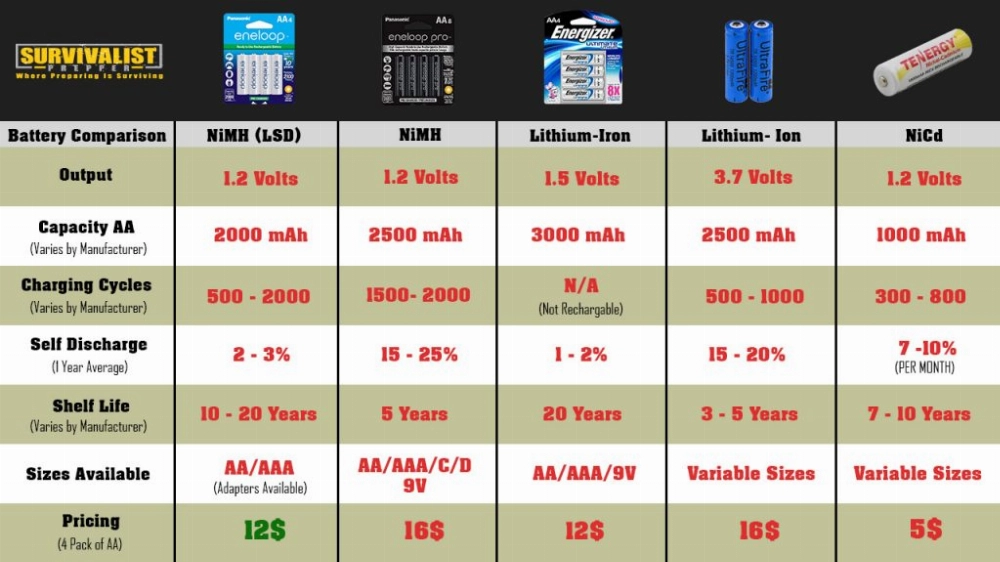
NiMH batteries are a middle-ground option between alkaline and lithium-ion. They’re rechargeable and more environmentally friendly, commonly found in medium-power LED lights like outdoor solar lights. They offer the following advantages:
- Rechargeable – can be used hundreds of times
- Higher capacity than alkaline batteries
- More environmentally friendly than disposable alkaline batteries.
On the downside, NiMH batteries tend to lose their charge faster when not in use compared to lithium-ion batteries.
4. Lead-Acid Batteries

Lead-acid batteries are often used for large LED systems, such as emergency lighting or off-grid solar setups. Despite their size, they offer advantages in specific applications:
- Cost-effective for high-capacity needs
- Proven and reliable technology.
- Capable of delivering high current when needed
Part 2: Battery Voltage for LED Lights
Voltage is crucial for LED lights; much like water pressure in a pipe, it drives the electrical current through the LED. Using the correct voltage is essential for optimal LED performance and lifespan. Here’s a breakdown of common voltage ranges:
1.2V to 1.5V
This voltage range is common for single-cell batteries like AA or AAA. You’ll find it in:
- Small LED flashlights
- Battery-powered fairy lights
- LED tea lights
3V to 3.7V
Batteries in this range are often used for:
- Larger LED flashlights
- Smartphone camera flashes
- Various household LED light bulbs.
6V to 12V
For more powerful lighting, these voltages are common in:
- Outdoor LED floodlights
- Automotive interior LED lighting
- Certain types of LED strip lights
It’s important to note that many LED systems include a driver or controller that regulates the voltage from the battery, ensuring the LED receives the correct voltage while protecting it from fluctuations and extending its lifespan.
Part 3: Key Considerations for Choosing LED Light Batteries: Key Parameters
When selecting batteries for LED lights, there are other important parameters to consider besides voltage.
Capacity
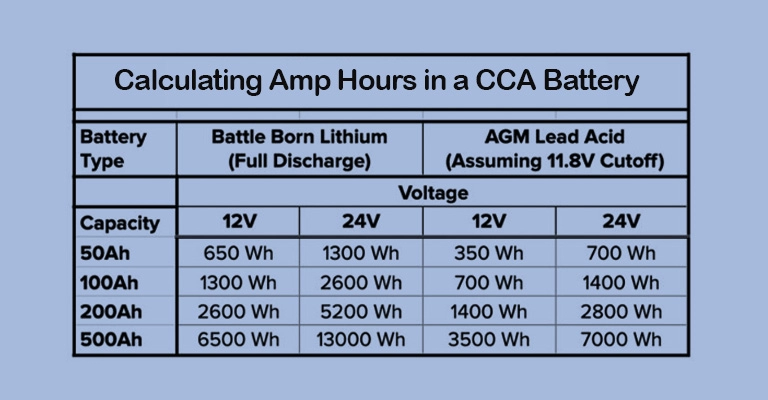
Capacity, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or ampere-hours (Ah), indicates how much electrical charge a battery can hold. This is analogous to a fuel tank’s capacity. The higher the capacity, the longer the runtime, but it also means a larger and heavier battery. For example, a 2000mAh battery will provide roughly twice the runtime of a 1000mAh battery.
Part 1: Introduction to LED Light Batteries
Choosing the right battery for your LED lights can significantly improve their performance and lifespan. With a variety of options available, it’s important to understand the different types of batteries and the advantages of each. Let’s explore the key factors to consider when selecting the perfect battery for your needs.
Part 2: Types of Batteries for LED Lights
There are several types of batteries commonly used in LED lights, each with its own unique advantages:
1. Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries are the most common and are well-suited for low-power devices. They are affordable and readily available, but they are not rechargeable, meaning they need to be replaced once they are depleted.
Pros:
- Cost-effective and easy to find
- Reliable and readily available for low-power LED lights
Cons:
- Not rechargeable
- Environmentally impactful due to frequent replacement
Suitable for: LED light strips, LED candles, night lights, and other low-power LED applications.
2. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are rechargeable and known for their high energy density, delivering more power in a compact form.
Pros:
- Rechargeable and long-lasting
- High energy density and efficiency
- Lightweight
Cons:
- More expensive
- Sensitive to extreme temperatures
Suitable for: High-end LED flashlights, portable LED work lights, and rechargeable headlamps.
3. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries offer a good balance of price, rechargeability, and performance. They are commonly used in mid-range LED devices and can be recharged hundreds of times before needing replacement.
Pros:
- Rechargeable
- Environmentally friendly
- Good performance for medium-power devices
Cons:
- Higher self-discharge rate than Li-ion batteries
- Slightly lower capacity than Li-ion batteries
Suitable for: Solar-powered garden lights, LED camping lanterns, and wireless LED wall sconces.
4. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are often used in larger, stationary setups like emergency lighting and off-grid solar LED systems. While not as energy-dense as Li-ion batteries, they are still reliable for more sustained power in large installations.
Pros:
- Reliable for large stationary systems
- Cost-effective
- Mature technology
Cons:
- Bulky
- Less efficient than modern battery types
Suitable for: Off-grid solar setups, emergency lighting systems, and large outdoor LED displays.
Part 3: Key Battery Characteristics
When evaluating batteries for LED lights, consider the following factors:
Discharge Rate
This refers to how quickly a battery can release its stored energy. High-power LEDs, like those in powerful flashlights, require batteries with a high discharge rate for optimal performance.
Cycle Life
Cycle life is the number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its performance starts to degrade. Rechargeable batteries with a longer cycle life offer better value over time.
Self-Discharge Rate
This is the rate at which a battery loses charge when not in use. NiMH batteries tend to have a higher self-discharge rate compared to Li-ion batteries, which can be an important consideration for LED lights that are not used frequently.
Operating Temperature Range
Batteries perform differently at extreme temperatures. If you use your LED lights outdoors in varying climates, choose batteries that perform well in both hot and cold conditions.
Size and Weight
For portable LED lights, the size and weight of the battery are crucial factors. Smaller and lighter batteries may be preferred, even if it means sacrificing some capacity.
Safety Features
Look for batteries with built-in protection against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. These features ensure that your LED lights are safe and operate optimally.
Energy Density
Energy density refers to how much power a battery can store in a given space. Batteries with higher energy density can deliver more power in a smaller and lighter package.
Part 4: Which Battery Type is Best?
The best battery for your LED lights depends on your specific needs. Here’s a breakdown:
For Portability and High Performance:
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are ideal for portable, high-performance applications. They are lightweight, offer high capacity, and can be recharged many times.
Suitable for:
- High-end LED flashlights
- Portable LED work lights
- Rechargeable LED headlamps
For Everyday Use and Economy:
If you need an affordable and reliable solution for everyday LED lighting, alkaline batteries are a good choice. While not rechargeable, they are well-suited for low-power devices.
Suitable for:
- Remote controls for LED light strips, battery-powered LED candles, and low-power LED night lights, among others.
For Rechargeable Convenience and Good Capacity:
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries offer a good balance: rechargeability and reliable performance at a reasonable price.
Suitable for:
- Solar-powered garden LED lights
- LED camping lanterns
- Wireless LED wall sconces
For Large, Stationary Setups:
While not as advanced as Li-ion batteries, they are ideal for off-grid systems and emergency lighting applications.
Suitable for:
- Emergency LED lighting systems
- Off-grid solar LED setups
- Large outdoor LED displays
Part 5: How Long Do LED Light Batteries Last?
The lifespan of LED light batteries varies depending on the battery type, usage, and environmental conditions. Here’s an overview:
Alkaline Batteries:
- Low-Power Devices: Lasts 6 months to a year
- Medium-Power Devices: Lasts a few hours to a few days
- Shelf Life: Up to 10 years when stored properly
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries:
- Cycle Life: 300-500 full charge cycles, lasting several years
- High-Power Devices: Lasts a few hours to a few days
- Shelf Life: Retains about 80% of charge after one year of storage
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries:
- Cycle Life: 300-500 charge cycles
- Medium-Power Devices: Lasts a few hours to a few days
- Shelf Life: Loses about 20% of charge per month when not in use
Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Cycle Life: 200-300 deep cycles for heavy-duty applications
- Ideal for: Large, stationary LED setups like off-grid systems
- Shelf Life: Relatively long when stored properly

## Part 5: Battery Life
LED and Battery Compatibility
When using LEDs and batteries, ensure they are compatible for efficient operation to prevent damage.
1. LED Specifications:
- Forward Voltage (Vf): LEDs require a specific forward voltage to operate correctly, typically ranging from 1.8V to 3.3V. The battery voltage should be compatible with the LED’s forward voltage requirements. Any mismatch can lead to LED failure or burnout.
- Forward Current (If): LEDs require a specific current to achieve their intended brightness. Exceeding this current can damage the LED. Always check the “Forward Current” specification (If) on the datasheet to ensure compatibility.
- Polarity: LEDs have polarity, meaning they have a positive (anode) and negative (cathode) terminal. Incorrect polarity can prevent the LED from lighting or even cause damage. The anode is typically the longer lead on the LED, while the cathode is the shorter lead. The datasheet will provide a diagram to guide you.
2. Battery Specifications:
- Voltage (V): Batteries provide a specific voltage. Common voltages include 1.5V (AA, AAA), 3.7V (Li-ion), 9V, and 12V.
- Capacity (mAh or Ah): This indicates the battery’s charge capacity, directly affecting the LED’s runtime. However, it does not directly impact the voltage.
- Type: The battery type (Alkaline, NiMH, Lithium-Ion, etc.) is important as it affects voltage stability and discharge behavior.
3. Compatibility Determination Considerations:
- Voltage Matching: The battery voltage should be close to the LED’s forward voltage. If the battery voltage is too high, a resistor is typically required to safely reduce the voltage.
- Current Limiting: A current-limiting resistor is necessary to prevent LEDs from drawing excessive current, which can cause damage. The resistor value should be calculated based on the battery voltage, LED forward voltage, and forward current. Various online calculators and formulas can help determine the correct value.
- Polarity: Ensure the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the anode (longer lead) of the LED and the negative terminal to the cathode (shorter lead).
4. Selecting the Appropriate Battery for Your LED:
- Small LEDs (e.g., Indicator Lights): For small LEDs, button cell batteries (e.g., CR2032) can be used with an appropriate resistor. For higher voltage sources, a resistor is necessary to ensure safe operation.
- High-Power LEDs (e.g., Flashlights): High-power LEDs require more current and typically need rechargeable batteries such as 3.7V Lithium-Ion batteries. When using multiple batteries, connecting them in series can provide the necessary voltage; however, an appropriate resistor is essential.
Related Tags:
- Ufine
- Electronics Engineer
For deeper insights into battery technology, refer to our guide: Lithium Battery Guide for Diesel to Electric Projects.

11.1V Lithium Polymer Battery: Features, Advantages, and Applications Explained
The 11.1V lithium polymer battery is a versatile power source used in various applications, including remote control models, drones, and other devices. This guide highlights its key features, advantages, and common uses.
Key Features
- Voltage: 11.1V, providing a stable power output suitable for high-performance applications.
- Lightweight: High energy density provides significant power in a lightweight and compact design.
- Rechargeable: These batteries are easy to recharge, making them an efficient power solution for repeated use.
Advantages
- Longer Run Time: 11.1V lithium polymer batteries provide extended usage compared to other battery types.
- Quick Charging Time: Rapid charging gets you back in action quickly.
- Stable Performance: Consistent performance under various conditions makes lithium polymer batteries a reliable choice for demanding tasks.
Common Applications
- Remote Control Models: Their compact size and high power output make 11.1V lithium polymer batteries ideal for remote control vehicles.
- Drones: The lightweight design and long-lasting power make them ideal for drone enthusiasts and professionals.
- Other Electronics: This battery type is also found in various other electronic devices that require an efficient power source.
Choose the 11.1V lithium polymer battery for the perfect blend of power, portability, and performance. The 11.1V lithium polymer battery is recommended by KHZH for reliable, high-performance electronic solutions.