Welcome to KHZH, where we delve into the fascinating world of battery technology. Today, we’ll explore the key differences between power batteries and energy batteries, breaking down their primary functions, types, and characteristics. Join us as we delve into these two crucial battery types.
Part 1: What is a Power Battery?
A power battery, also known as a high-power battery, is a rechargeable energy storage device designed to deliver rapid bursts of power. Unlike energy batteries, which focus on long-term energy storage, power batteries are specifically engineered for high-power output, providing quick surges of energy when needed. These batteries are commonly used in applications such as electric vehicles, power tools, and systems requiring rapid acceleration or handling heavy loads.
Key Functions:
- Provides quick bursts of energy when needed.
- Delivers stable power output for high-demand applications.
- Enables rapid charging and discharging cycles.
- Supports devices requiring sudden power surges, such as electric vehicles and power tools.
Types:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Known for their high energy density and lightweight nature, lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in power applications, including electric vehicles, portable electronics, and energy storage systems.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: These batteries are known for their durability and ability to handle frequent charging and discharging cycles. NiMH batteries are commonly used in power tools, hybrid vehicles, and certain portable electronics.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Lead-acid batteries, while not typically classified as high-power, are still used in various power applications. These include automotive starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) systems. Their reliability and cost-effectiveness also make them suitable for backup power systems in telecommunications and emergency lighting.
Characteristics:
- High power output capability.
- Fast charging and discharging rates.
- Ability to withstand frequent charge and discharge cycles.
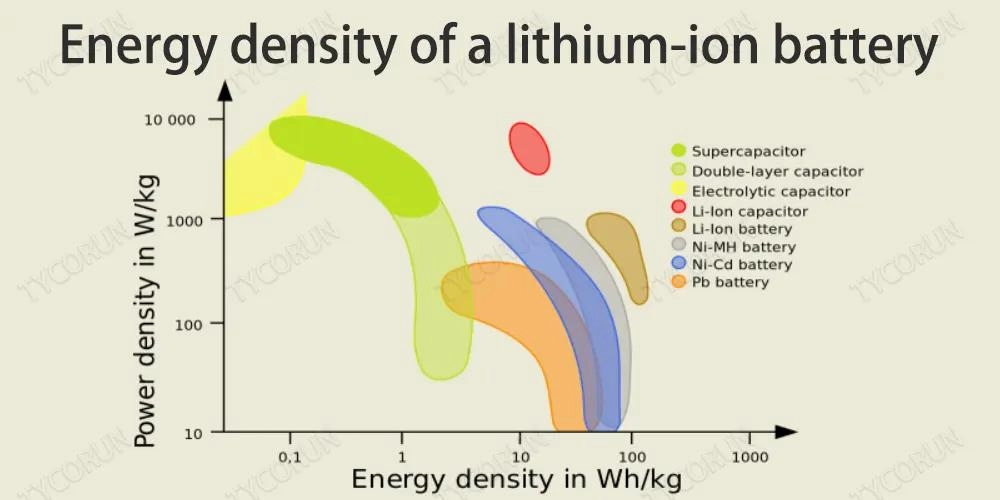
- Lower energy density compared to energy batteries.
- Utilizes chemistries like lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride, optimized for high-power performance.
Part 2: What is an Energy Battery?
An energy battery, also known as a high-energy battery, is a rechargeable device designed to store and release energy over extended periods. These batteries are ideal for applications that require sustained power output and long-term energy storage. Energy batteries prioritize efficiency and reliability for long-duration use.
Key Functions:
- Stores energy for extended periods.
- Provides a stable, consistent power supply.
- Supports devices and systems requiring continuous operation for extended periods.
- Supports portable electronics, renewable energy systems, and backup power solutions.
Types:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Known for their durability and cost-effectiveness, lead-acid batteries are widely used in off-grid solar systems, backup power, and emergency lighting.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries, highly favored for their high energy density and long cycle life, are used in residential and commercial energy storage systems, electric vehicles, and portable electronics. For more information on how to safely charge these batteries, check out our charging tips.
- Flow Batteries: Using liquid electrolytes stored in external tanks, these batteries offer scalability and long-term energy storage. They are ideal for grid storage and integration of renewable energy sources.
- Sodium-Sulfur (NaS) Batteries: These high-temperature batteries have significant energy storage capacity and are well-suited for grid storage and industrial-scale applications.
- Nickel-Iron Batteries: Their durability and ability to withstand deep discharges make these batteries common in off-grid applications and renewable energy storage systems.
Characteristics:
- High energy density, allowing for efficient storage of large amounts of energy.
- Slow discharge rate, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply for extended periods.
- They have a longer lifespan compared to power batteries because they are optimized for charge and discharge cycles.
- They utilize chemistries like lithium-ion and lead-acid to enhance energy storage capabilities.
- Ideal for applications requiring continuous power output.
At KHZH, we are dedicated to helping you understand the unique roles and applications of different battery types. With power batteries providing quick bursts of energy and energy batteries catering to long-term power needs, each type has its specific use cases and advantages. Whether you’re looking for batteries for electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, or power tools, understanding these differences is key to making the right choice for your needs. A thorough understanding of these critical differences empowers you to select the optimal battery solution for any application.
Power Batteries vs. Energy Batteries: Key Differences & Use Cases | KHZH
Part 3: What Is the Difference Between Power and Energy Batteries?
Aspect Comparison Table
| Aspect | Power Batteries | Energy Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide high-energy bursts, suitable for rapid acceleration or powering heavy loads | Long-term energy storage, continuous power output |
| Power Output | High, rapid energy release | Stable, provides consistent energy over time |
| Charging/Discharging Rates | Fast charging/discharging | Slower charging/discharging |
| Energy Density | Lower energy density | Higher energy density |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifespan, faster degradation | Longer lifespan due to efficient charging/discharging management |
| Applications | Electric vehicles, power tools, emergency systems | Portable electronics, renewable energy storage, backup power |
| Chemistry | Lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride | Lithium-ion, lead-acid, nickel-cadmium |
Detailed Breakdown
Purpose
Power batteries release high energy quickly, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid acceleration or heavy-duty power output.
In contrast, energy batteries focus on long-term energy storage and a sustained, stable power supply, making them ideal for continuous operation over extended periods.
Power Output
Power batteries provide rapid energy release, enabling them to provide power immediately when needed.
On the other hand, energy batteries provide a consistent and stable energy flow, ensuring long-term functionality.
Charging & Discharging Rates
Power batteries support fast charging and discharging, enabling quick energy replenishment and high-power bursts.
However, energy batteries charge and discharge more slowly, which helps optimize energy retention and efficiency.
Energy Density
Power batteries generally have lower energy density because they prioritize rapid power output over energy storage.
Energy batteries have higher energy density, maximizing energy storage within a given size or weight.
Lifespan
Due to frequent high power demands, power batteries degrade faster and typically have a shorter lifespan.
Energy batteries are designed for optimized charge-discharge cycles, which extends their lifespan through efficient energy management.
Applications
- Power batteries: Ideal for electric vehicles (EVs), power tools, emergency backup systems, and hybrid electric vehicles (HEV).
- Energy batteries: Commonly found in portable electronics, renewable energy storage, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Chemistry
Power batteries use materials optimized for high power performance, such as lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH).
Energy batteries use chemistries suitable for efficient long-term energy storage, including lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-cadmium (NiCd).
Part 4: Power Battery vs. Energy Battery – Use Cases & Applications
Power Battery Use Cases
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) – Provides rapid energy bursts for acceleration and enhanced performance.
- Power Tools – Provides high-energy bursts for cordless drills, saws, and other heavy-duty tools.
- Emergency Systems – Used in hospitals and telecommunication facilities to provide critical backup energy.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) – Stores energy from regenerative braking and provides power during acceleration.
- Aerospace – Essential for satellites and spacecraft, providing power for communication, navigation, and experiments.
- Grid Stabilization – Helps balance the power grid by managing peak energy demands.
Energy Battery Use Cases
- Portable Electronics – Powers smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other devices for long-lasting usage.
- Renewable Energy Storage – Stores excess power from solar panels and wind turbines, improving energy reliability.
- Backup Power Systems – Provides a continuous power supply for data centers, homes, and industries.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supplies) – Ensures stable energy supply during power outages, protecting sensitive electronic equipment.
- Off-Grid Power Solutions – Enables energy independence in remote locations through sustainable storage.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between power batteries and energy batteries is crucial for selecting the right solution for specific applications.
While power batteries excel at providing rapid bursts of energy, energy batteries ensure a long-term, consistent power supply—each playing a unique role in modern energy storage and applications.
For high-performance energy solutions, KHZH offers cutting-edge battery technology designed to meet the needs of various industries.
Off-Grid Power Solutions and Applications
Off-Grid Power Solutions: Key to Remote Energy Systems
Off-grid power systems are crucial for remote areas or locations not connected to the main power grid. They are ideal for cabins, RVs, or any self-sufficient premises where access to traditional electricity is difficult or impossible.
Residential Energy Management: Efficient Energy Use
Home energy storage systems, such as home batteries, help optimize energy usage in homes. These systems allow homeowners to store electricity for later use, reducing energy costs. At the same time, they also enable better utilization of renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on the grid.
Marine and RV Applications: Quiet, Clean Energy
Off-grid battery solutions significantly enhance the user experience for marine and RV applications. These clean, quiet systems are ideal for powering boats, yachts, and RVs, providing an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional generators.