Choosing the right battery can be daunting, given the vast array of options available. In this article, we will compare silver-zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries. We will explore their composition, performance, and applications to help you make an informed decision about which battery is best suited for your needs.

Part 1: Silver-Zinc Batteries
Silver-zinc batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses silver oxide and zinc as its primary materials. These batteries are known for their high energy density and reliable performance, making them ideal for applications where reliable power is mission-critical.
Composition and Working Principle
- Positive Electrode: Silver Oxide (AgO)
- Negative Electrode: Zinc (Zn)
- Electrolyte: Alkaline solution, typically potassium hydroxide (KOH)
During discharge, the zinc negative electrode releases electrons, which flow through an external circuit to the silver oxide positive electrode. The silver oxide is reduced to silver, while the zinc is oxidized to zinc oxide. This flow of electrons generates an electric current that powers the device. Charging reverses this reaction, restoring capacity.
Characteristics
- High Energy Density: Delivers more power in a smaller volume.
- Reliable Performance: Ensures consistent output and efficiency.
- Shorter Lifespan: Silver-zinc batteries have a relatively shorter lifespan compared to other rechargeable batteries.
- Lightweight Design: Makes them easy to transport and integrate into various devices.
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses fewer toxic materials, making it more eco-friendly.
Advantages
- High Energy Output: Suitable for high-drain applications.
- Compact and Lightweight: Ideal for portable and space-constrained devices.
- Safe and Stable: Reduced risk of leaks and thermal runaway.
- Environmentally Friendly: Easier to recycle and less harmful to the environment.
Disadvantages
- High Production Cost: Due to the silver content, these batteries are expensive to manufacture.
- Short Lifespan: They have a limited number of charge cycles.
- Maintenance Requirements: Requires more frequent replacement than some alternatives.
Common Applications
- Military Equipment: Used in communication devices and critical tools.
- Aerospace Devices: Powers instruments and systems in spacecraft.
- Medical Devices: Used in portable medical equipment and implants.
- Hearing Aids: Favored for their small size and powerful output.
- High-Performance Drones: Selected for their lightweight and energy needs.
Part 2: Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Batteries
Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries commonly come in cylindrical and prismatic shapes. Lithium ions act as charge carriers during both charging and discharging. These batteries are widely used in various electronic devices due to their high energy density and extended cycle life.
Composition and Working Principle
- Negative Electrode: Typically made of carbon-based materials such as graphite, lithium titanate, or silicon.
- Positive Electrode: Usually composed of lithium metal oxides such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), or lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4).
- Electrolyte: A lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent or within a polymer electrolyte matrix.
During the discharge cycle, lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the electrolyte, creating an electric current that powers the device. Charging the battery reverses this process, with lithium ions moving back from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
Characteristics
- High Energy Density: Provides longer-lasting power in a compact size.
- Stable Voltage Output: Maintains a consistent voltage throughout the discharge cycle.
- Longer Cycle Life: Offers a longer lifespan compared to other rechargeable batteries.
- Lightweight Design: Ideal for portable electronics.
- Susceptible to Overcharging: Overcharging can cause damage.
Advantages
- Longer Run Time: High energy density allows for longer intervals between charges.
- Lightweight and Compact: Perfect for portable devices.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: Offers a significantly longer shelf life.
To further understand the benefits of different types of batteries, check out our guide on LiFePO4 batteries, LiFePO4 batteries, known for their safety and long lifespan, are another popular choice for various applications.
Silver-Zinc vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Comparison
Advantages of Silver-Zinc Batteries
- High Energy Density: Silver-zinc batteries are known for their high energy density, making them well-suited for applications requiring efficient energy storage.
- Rechargeable: These batteries are rechargeable and can provide multiple cycles of use before their performance degrades.
- Environmental Impact: Silver-zinc batteries are easier to recycle and contain fewer hazardous materials compared to other battery types.
- Safety: Generally safer, silver-zinc batteries have a lower risk of thermal runaway or explosion compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Disadvantages of Silver-Zinc Batteries
- Limited Cycle Life: Silver-zinc batteries typically offer 150 to 300 charge cycles before significant capacity degradation.
- Size and Weight: Although relatively lightweight, silver-zinc batteries are generally bulkier than lithium-ion batteries, making them less suitable for compact devices.
- High Cost: The silver content in these batteries makes them more expensive to produce than many other battery types, which can be a significant factor for some applications.
- Slow Charging Speed: Silver-zinc batteries generally charge slower than lithium-ion alternatives, leading to longer wait times for recharging.
Advantages of Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Batteries
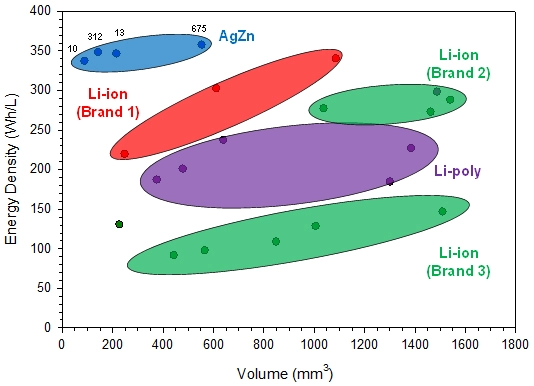
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries offer a higher energy density (150 to 250 Wh/kg) compared to silver-zinc, translating to longer run times.
- Longer Cycle Life: Lithium-ion batteries can average over 500 charge cycles, with high-end models exceeding 1000 cycles, making them durable and cost-effective in the long run.
- Compact and Lightweight: Lithium-ion batteries are significantly smaller and lighter than silver-zinc batteries, making them ideal for portable devices and electric vehicles.
- Fast Charging: Lithium-ion batteries are known for their fast charging capabilities, efficiently reducing charge times and minimizing downtime.
Disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Aging: Lithium-ion batteries are prone to aging, which leads to a decrease in capacity over time.
- Thermal Runaway Risk: Improper handling or damage can lead to dangerous thermal runaway and fire risks.
- Production Costs: Although lithium-ion batteries are often more cost-effective in the long run, their initial production costs can be higher than some other battery types.
- Protection Circuitry: Lithium-ion batteries require protection circuitry to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, adding complexity to design and usage.
Common Applications of Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Smartphones and Tablets: Due to their high energy density and compact form, lithium-ion batteries are widely used in mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
- Laptops: These batteries provide the portable power needed for laptops, allowing for extended operation on a single charge.
- Electric Vehicles: Lithium-ion batteries are used to power electric vehicles, providing reliable power for long-distance travel.
- Power Tools: Cordless tools, such as drills and saws, benefit from lithium-ion batteries’ lightweight design and efficient energy output.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Lithium-ion batteries are often integrated into energy storage systems for solar and wind power, providing a reliable way to store electricity.
Comparison of Silver-Zinc vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Energy Density
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: 100 to 150 Wh/kg
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: 150 to 250 Wh/kg
Lithium-ion batteries offer a higher energy density, providing longer run times between charges.
Weight and Size
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Relatively light in weight, but bulkier in size
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: More compact and lightweight
Cycle Life
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: 150 to 300 cycles
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: 500 to 1000+ cycles
Lithium-ion batteries generally offer a longer cycle life.
Cost
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Expensive due to silver content
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Higher initial cost, but cost-effective in the long run
Silver-zinc batteries have a higher upfront cost; lithium-ion batteries are more cost-effective over time due to their longer lifespans.
Environmental Impact
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Easier to recycle and have a lower environmental impact, while lithium-ion batteries present significant recycling challenges.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Require careful handling and recycling due to materials like lithium and cobalt
Application Range
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Used in military, aerospace, and medical equipment
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems
Silver-zinc batteries are often used in specialized, high-reliability applications, while lithium-ion batteries are more common in everyday consumer devices.
Safety
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Safer, with a lower risk of thermal runaway
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Risk of thermal runaway, requiring advanced safety features
Lithium-ion batteries require robust safety systems to prevent hazards such as thermal runaway, whereas silver-zinc batteries are inherently more stable.
Charging Speed
- Silver-Zinc Batteries: Slower charging speed
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Fast charging capabilities
Lithium-ion batteries offer faster charging times, providing more convenience for users.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are zinc batteries better than lithium-ion?
Zinc batteries may be preferable in applications where cost and safety are paramount, while lithium-ion batteries offer superior energy density and cycle life.
Will zinc batteries replace lithium-ion?
Due to performance and application differences, zinc batteries are unlikely to completely replace lithium-ion batteries. However, their inherent safety and lower cost may make them preferable in certain applications.
Are silver-zinc batteries rechargeable?
Yes, silver-zinc batteries are rechargeable and can be used for multiple cycles before their performance degrades.
How Long Do Zinc Batteries Last?
The lifespan of a zinc battery depends on various factors, such as usage, discharge rate, and environmental conditions. On average, zinc batteries can last from several months to a few years.
Related Topics:
- Deep Cycle Battery Charging Guide
Unsure how to charge a deep cycle battery? Our guide simplifies the process, providing safe and effective charging methods. - Battery Array vs. Single Battery: Which is Best for Your Energy Needs?
Understand the differences and benefits of battery arrays and single batteries to make the best choice for your energy needs. - What is a Battery Array?
A battery array is a connection of multiple batteries designed to provide stable and reliable power. This article explores its types, benefits, and key applications. - Growth Trends in Flexible Thin-Film and Printed Battery Markets
The flexible thin-film and printed battery market is rapidly evolving. This article covers the market’s growth, innovations, challenges, and future trends. - Optimizing Battery Charging Cycles: Extend Battery Life and Improve Performance
Learn how charging cycles affect battery life and performance. Discover tips and tools, such as using a battery charging calculator, to extend battery life.







