Traditional centralized solutions such as 1500V have replaced 1000V as the development trend. With the development of centralized photovoltaic power stations and energy storage towards larger capacities, DC high voltage has become the leading technical solution for reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Energy storage systems with a DC side voltage of 1500V are gradually becoming the trend. The 1500V energy storage system solution has a DC side voltage of 1000V-1500V. Taking the Sun power supply solution, for example, the battery system’s energy density and power density are increased by more than 35% compared to traditional solutions. For power stations of the same capacity, there are fewer devices, and the costs of devices such as battery systems, PCS, BMS, and cables are significantly reduced. Infrastructure and land investment costs are also reduced simultaneously, and it is estimated that initial investment costs can be reduced by more than 10%. However, simultaneously, the voltage of the 1500V energy storage system has increased, which has increased the number of batteries in series, making it more challenging to control consistency. Requirements such as prevention and protection against the risk of DC arcing and electrical insulation design have also become more stringent.

Distributed solutions are the most efficient, and their market share is expected to increase rapidly. Compared with centralized technical solutions, the DC side of the battery cluster is connected in parallel via a distributed string inverter, which is converted to the AC side in parallel. This avoids the problems of parallel loop current, capacity loss, and the risk of DC arcing if the DC side is connected in parallel and improves operational safety. At the same time, control accuracy changes from multiple battery clusters to a single battery cluster, which is more efficient.
The intelligent string solution uses a control strategy of one cluster, one management, one package, and one optimization, which Huawei first introduced. The features of the intelligent string solution are as follows:
- Stringing: Energy optimizers are used to achieve cell module-level management, cell cluster controllers are used to attain inter-cluster balancing, and distributed air conditioners reduce the temperature difference between clusters.
- Intelligent: Advanced ICT technologies such as AI and cloud BMS are applied to the internal short circuit detection scenario, AI is used to predict the battery status, and a multi-model linkage intelligent temperature control strategy is used to ensure optimal charging and discharging status.
- Modularization: The battery system is modularized, and faulty modules can be cut off individually without affecting the regular operation of other modules in the cluster. The PCS is modularized so that when a single PCS fails, the others can continue to work, and when multiple PCSs fail, the system can still operate.
The high-voltage cascade solution avoids parallel connection and improves system efficiency. The high-voltage cascade solution adopts the topology of an SVG to directly achieve 6kV/10kV/35kV AC high voltage through multiple cells connected in series, eliminating the need for a transformer. The advantages are as follows:
- Safety: There is no parallel connection of cells in the system. If some cells are damaged, the scope of replacement is narrow, the impact is small, and maintenance costs are low.
- Consistency: The absence of parallel structures avoids battery circulation problems. The internal balancing control between cells in the battery cluster is achieved through the BMS, which can maximize the utilization of cell capacity. Fewer cells can be installed with the same amount of grid-connected power on the AC side, reducing the initial investment.
- High efficiency: As the system does not operate with cells/battery clusters in parallel, there is no short board effect. The system life is approximately equal to the single-cell life, which maximizes the operating economy of the energy storage device. The system does not require a step-up transformer, and the on-site system cycle efficiency can reach 90%.
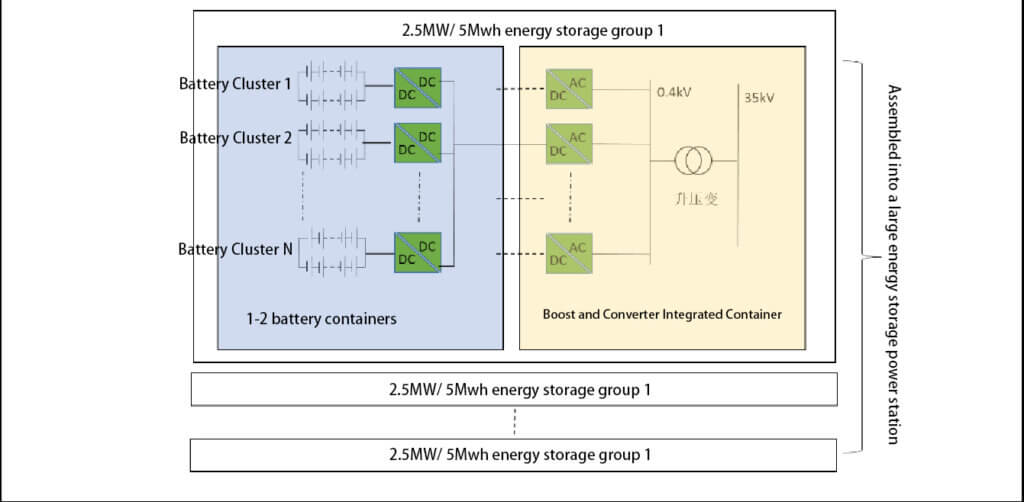
The distributed solution improves safety through DC isolation. In addition to the traditional centralized solution, a DC/DC converter is added at the outlet of the battery cluster to isolate the battery cluster. After collection, the DC/DC converter is connected to the DC side of the centralized PCS, and 2 to 4 PCS are connected in parallel to a local transformer. After being boosted by the transformer, the power is connected to the grid. Adding DC/DC isolation in the system avoids the DC arcing, circulating currents, and capacity losses that would otherwise occur when DCs are connected in parallel, significantly improving system safety and thus efficiency. However, since the system needs to go through two stages of inversion, this reverse affects system efficiency.
Table of Contents
Energy Storage System: Ensuring Safety and Improving Efficiency
- Energy Storage System Classification: Centralized, Distributed, Intelligent String, High-Voltage Cascade, Distributed-Centralized
- Energy Storage Technical Routes Focus on safety, cost, and efficiency
Energy storage integration technology route: Topology solutions gradually iterate
- Centralized solution: 1500V replaces 1000V as the trend
- Distributed solution: High efficiency, mature solution
- Intelligent string solution: One package, one optimization, one cluster, one management
- High voltage cascade solution: An efficient solution without a parallel structure
- Distributed solution: DC isolation + centralized inverter
- Summary: Comparison of technology routes
Energy Storage System: Ensuring Safety and Improving Efficiency
An electrochemical energy storage system consists of two main parts: the DC side and the AC side. The DC side is the battery compartment, which includes equipment such as batteries, temperature control, fire protection, a combiner box, and a container. The AC side is the electrical compartment, which includes an energy storage converter, a transformer, and a container. The batteries on the DC side generate direct current (DC). To interact with the power grid, direct current must be converted to alternating current (AC) via a converter.
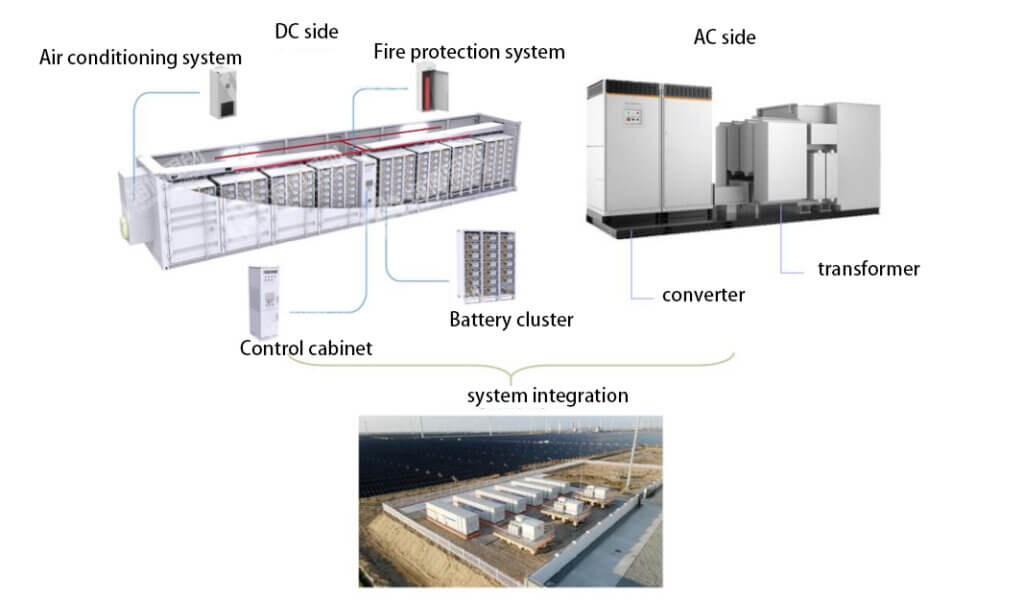
Energy storage system classification: centralized, distributed, intelligent string, high-voltage cascaded, decentralized
Large energy storage systems can be divided into the following categories based on their electrical structure:
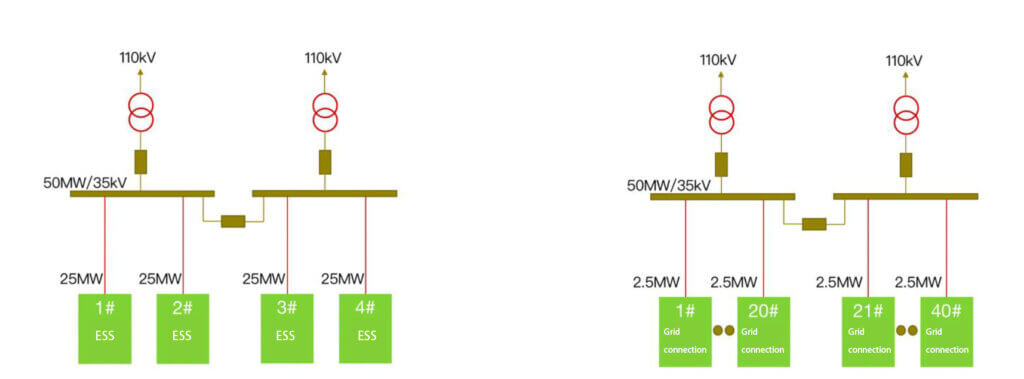
Centralized: a centralized grid-connected energy storage system with low voltage and high power boost, in which multiple clusters of batteries are connected in parallel and then connected to a PCS. The PCS pursues high power and high efficiency, and a 1500V solution is currently being promoted.
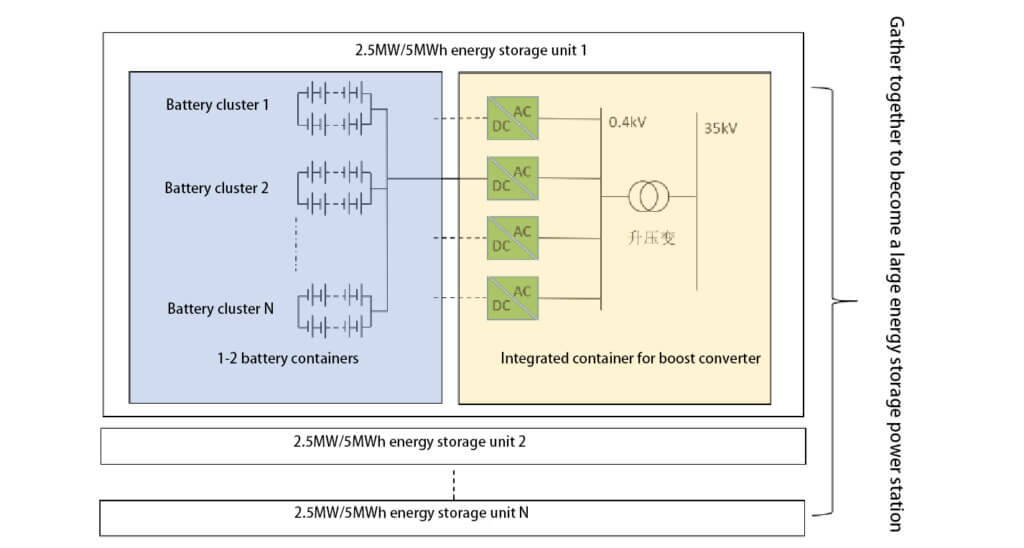
Distribute: Low-voltage, low-power distributed boost grid-connected energy storage system, each cluster of batteries is connected to a PCS unit, and the PCS uses a low-power, distributed arrangement.

Intelligent string: Based on the distributed energy storage system architecture, it adopts innovative technologies such as battery module-level energy optimization, battery single-cluster energy control, digital intelligent management, and fully modularized design to achieve more efficient application of the energy storage system.

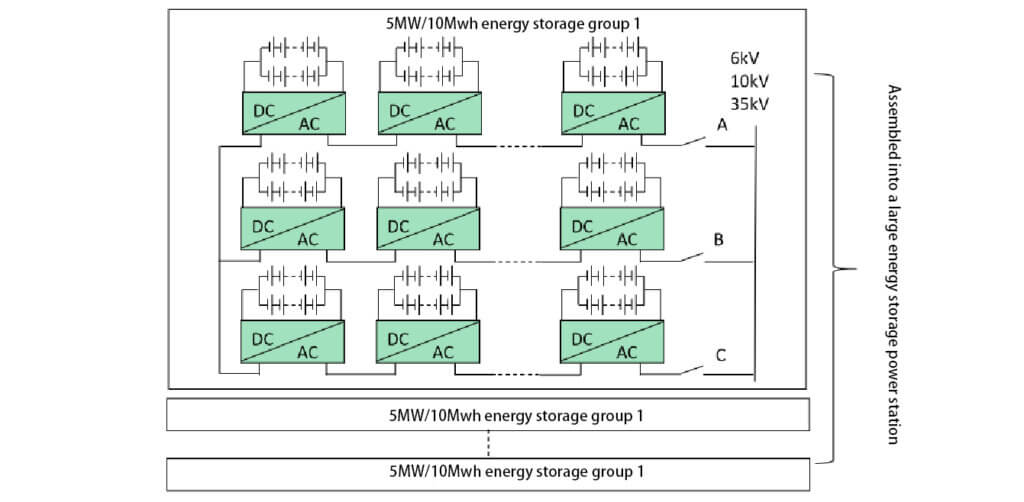
High-voltage cascaded high-power energy storage system: the battery is inverter-connected in a single cluster, without a transformer, and directly connected to the power grid at a voltage level of 6/10/35kV or higher. The capacity of a single unit can reach 5MW/10MWh.
Distributed: The DC side is connected in parallel with multiple branches. A DC/DC converter is added at the battery cluster outlet to isolate the battery cluster. The DC/DC converter is connected to the centralized PCS DC side after collection.
The iterative process of energy storage technology revolves around safety, cost and efficiency.
Safety, cost, and efficiency are the key issues that need to be addressed in the development of energy storage. The core of energy storage technology iteration is also to improve safety, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
(1) Safety
The safety of energy storage power stations is the industry’s biggest concern. Potential safety hazards of electrochemical energy storage power stations include electrical fires, battery fires, hydrogen explosions in the event of fire, and system abnormalities. The causes of safety issues with energy storage power stations can usually be traced back to thermal runaway in the batteries. The triggers of thermal runaway include mechanical abuse, electrical abuse, and thermal abuse. To prevent safety issues, the state of the batteries needs to be strictly monitored to avoid the triggers of thermal runaway.

(2) High efficiency
The consistency of the battery cells is a key factor affecting system efficiency. The consistency of the battery cells depends on the quality of the battery cells, the energy storage technology solution, and the operating environment of the battery cells. As the number of cycles of the battery cells increases, the differences between the battery cells gradually become apparent. When combined with the differences in the actual operating environment during operation, the differences between multiple battery cells will be exacerbated, highlighting the issue of consistency, posing a challenge to BMS management and even posing a safety risk.
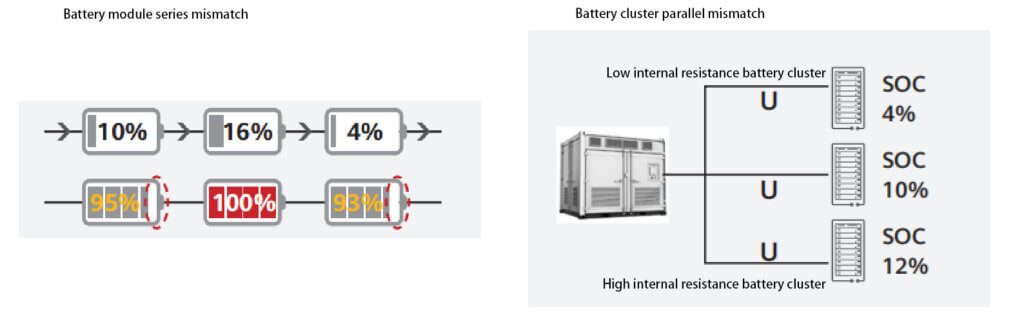
- Battery module mismatch in series: The available capacity of the cells in series can only reach the capacity of the weakest battery module, making it impossible to utilize the capacity of other batteries fully.
- Battery cluster mismatch in parallel: The available capacity of the battery clusters in parallel can only reach the capacity of the weakest battery cluster, making it impossible to utilize the capacity of other batteries fully.
- Differences in battery internal resistance cause circulation: Battery circulation causes the temperature of the battery cells to rise, which accelerates aging, increases system heat dissipation, and reduces system efficiency.
In the design and operation plan of the energy storage power station, the battery consistency should be improved as much as possible to improve system efficiency.
(3) Low cost
The cost of a low-cost energy storage system is related to the initial investment and the cycle life. The aging and degradation of battery materials, the charging and discharging regime, the operating temperature of the battery, and the consistency of the individual cells will all affect the cycle life of the battery. When the temperature difference between the batteries in the container is greater than 10 degrees, it will lead to a reduction in battery life of more than 15%. Differences in temperature rise between modules will also lead to a reduction in the overall system life. The energy storage system should improve the cycle life of the system by optimizing the charging and discharging methods, reducing the temperature difference between systems, and improving the consistency of the batteries.
Energy storage integration technology route
Centralized solution: 1500V replaces 1000V as the trend
With the development of centralized photovoltaic power stations and energy storage towards larger capacities, DC high voltage has become the main technical solution for reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Energy storage systems with a DC side voltage increased to 1500V are gradually becoming the trend. Compared to the traditional 1000V system, the 1500V system increases the withstand voltage of components such as cables, BMS hardware modules, and PCS from no more than 1000V to no more than 1500V. The 1500V technical solution for energy storage systems comes from PV systems. According to CPIA statistics, the market share of domestic PV systems with a DC voltage rating of 1500V in 2021 is about 49.4%, and it is expected to gradually increase to nearly 80% in the future. A 1500V energy storage system will help improve compatibility with PV systems.
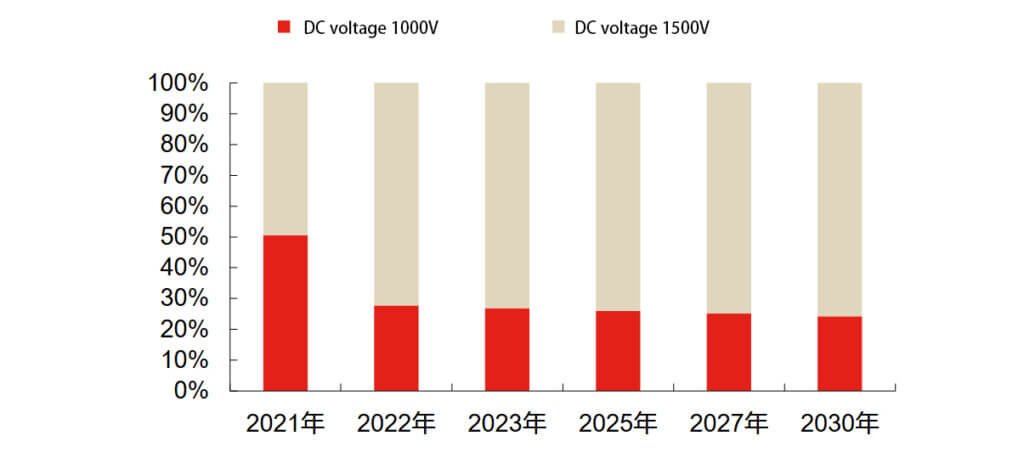
Looking back on the development of photovoltaic systems, increasing the DC side voltage to 1500V can reduce line losses on the AC and DC sides and losses in the low-voltage side windings of the transformer by using higher input and output voltage levels. This improves the efficiency of the power station system, increases the power density of the equipment (inverters, transformers), reduces the size, and reduces the workload in terms of transportation and maintenance, which is beneficial for reducing system costs. Take TBEA’s 1500V photovoltaic system solution released in 2016 as an example. Compared with the traditional 1000V system, the efficiency of the 1500V system is improved by at least 1.7%, the initial investment is reduced by 0.1438 yuan/W, the number of equipment is reduced by 30-50%, and the inspection time is shortened by 30%.
1500V energy storage system solution comparison The 1000V solution also has improved performance. Taking Sungrow’s solution as an example, compared with the 1000V system, the energy density and power density of the battery system have both increased by more than 35%. For a power station of the same capacity, there are fewer devices, and the costs of the battery system, PCS, BMS, cables and other equipment are greatly reduced, as are the investment costs for infrastructure and land. It is estimated that compared to traditional solutions, the initial investment cost of a 1500V energy storage system is reduced by more than 10%. However, at the same time, the increased voltage of the 1500V energy storage system increases the number of batteries in series, making it more difficult to control consistency. Requirements such as prevention and protection against the risk of DC arcing and electrical insulation design are also higher.

Distributed solution: high efficiency and mature solution
The distributed solution is also known as multi-branch parallel connection on the AC side. Compared with the centralized technical solution, the distributed solution connects the DC sides of the battery clusters in parallel via distributed string inverters to form an AC side parallel connection, avoiding the parallel loop current, capacity loss, and risk of DC arc caused by connecting the DC sides in parallel, and improving operational safety. At the same time, the control accuracy changes from multiple battery clusters to a single battery cluster, which is more efficient.
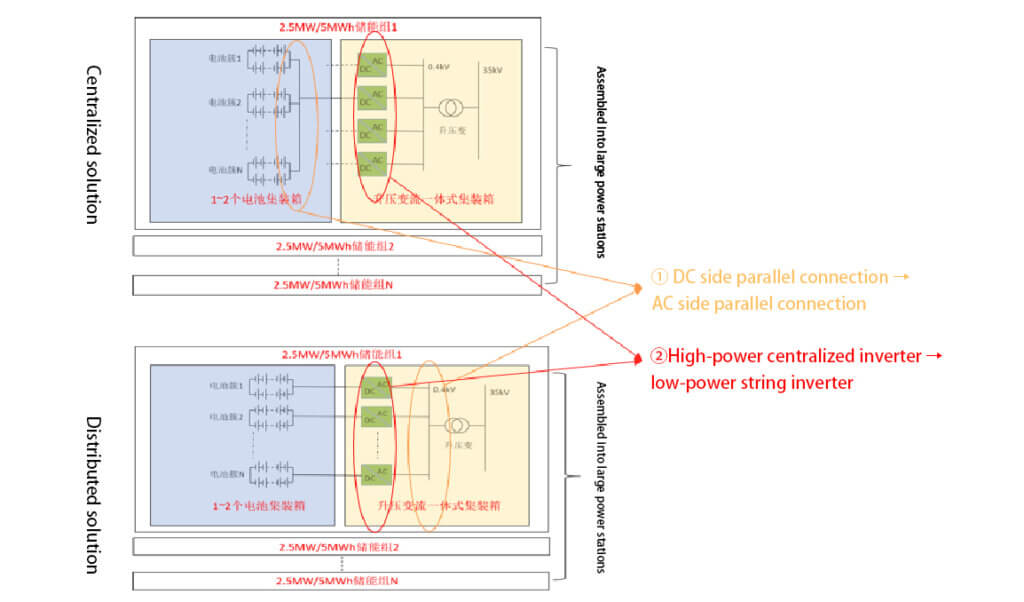
| Distributed | Centralized | |
| Modular system design | The PCS is modularly designed, ensuring high system availability | No modular design, PCS failure affects the entire container |
| Battery performance requirements | Low battery performance requirements, different branches support the mixed use of new and old batteries, avoiding the barrel effect, and the energy storage system maximize charging and discharging, which can achieve staged power replenishment. | Cannot support the mixing of new and old batteries, as the difference in internal resistance between new and old batteries causes circulation, which brings about heat and accelerates the aging of new batteries |
| Temperature control | Single cluster thermal management to ensure an even temperature field within the cluster | The temperature difference in the container can reach 10 degrees, which affects the life of the battery pack, as heat is dissipated centrally through 1-2 air conditioners |
| Discharge capacity | A multi-branch design is used to individually control the operation of each cluster of batteries, avoiding capacity loss due to circulation and increasing the discharge capacity over the life cycle. | The battery clusters are directly connected in parallel, and the difference between the clusters reduces the available capacity of the system for DC limiting |
Intelligent string solution
Huawei’s proposed intelligent string solution addresses three significant problems with centralized solutions:
(1) Capacity attenuation: In traditional solutions, there is a significant “short board effect” in battery use. Battery modules are connected in parallel. When charging, one battery cell is fully charged, and charging stops. When discharging, one battery cell is discharged, and discharging stops. The system’s overall life depends on the battery, which has the shortest life.
(2) Consistency: In the operation of energy storage systems, there are deviations in battery consistency due to different specific environments, resulting in an exponential attenuation of system capacity.
(3) Capacity mismatch: Parallel connection of batteries can easily lead to capacity mismatch, where the actual usable capacity of the battery is much lower than the standard capacity.
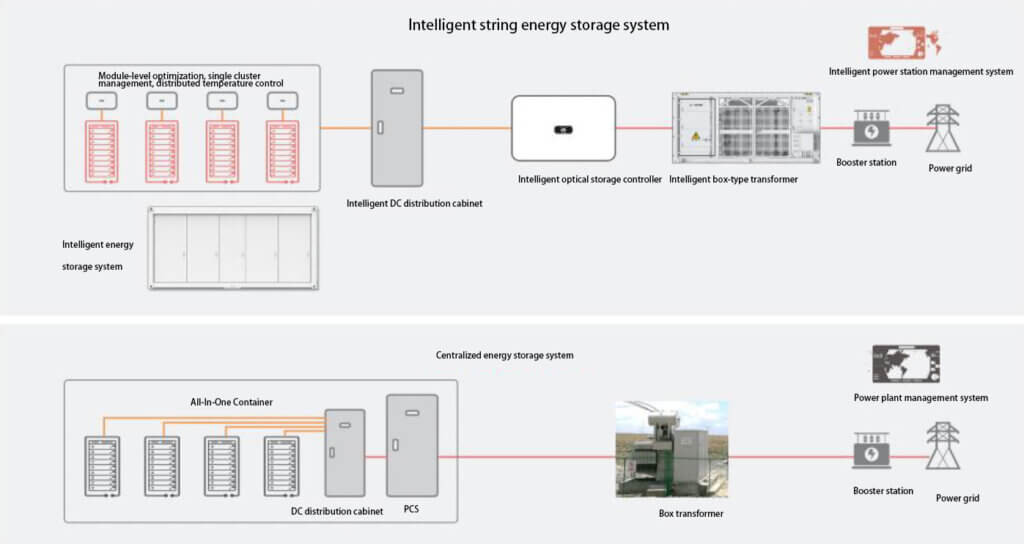
The intelligent string solution solves the above three problems of the centralized solution through a strong, intelligent, and modular design:
(1) String: Using energy optimizers to manage battery modules, cell cluster controllers to achieve cell-to-cell balancing, and distributed air conditioning to reduce cell temperature difference.
(2) Intelligent: Advanced ICT technologies such as AI and cloud BMS are applied to the internal short circuit detection scenario, AI is used to predict the battery status, and a multi-model linked intelligent temperature control strategy is used to ensure optimal charging and discharging status.
(3) Modularization: The battery system is modularized, and faulty modules can be cut off individually without affecting the regular operation of other modules in the cluster. The PCS is modularized so that when a single PCS fails, the other PCSs can continue to work, and when multiple PCSs fail, the system can remain operational.
| Dimension | Intelligent string energy storage solutions | Traditional centralized energy storage solutions |
| Higher Discharge | Higher discharge capacity. Adopting battery module-level energy optimizer to avoid capacity loss due to mismatch and increase discharge capacity by more than 6% during the life cycle: Adopting intelligent single-cluster battery cluster controller to prevent capacity loss due to loop current and increase discharge capacity by more than 7% during the life cycle. | There is no battery module equalization design, no optimization between battery modules within the cluster, no full discharge, module replacement requires manual equalization adjustment, battery clusters are directly connected in parallel, and no cluster voltage regulation; the difference between clusters will reduce the available capacity. |
| Better investment | Adopting high-density pre-set installation, the on-site delivery cost can be reduced by 1~3 cents/h; adopting single-cluster management, initial battery configuration can be reduced by more than 5%; adopting replenishment mode, compared with the traditional centralized solution, initial battery configuration can be reduced by more than 30% to achieve lower initial cost. | The initial and total investment is high, can’t replenish power, and needs to be over-allocated by 60-70% initially. |
| Intelligent temperature control | With an intelligent temperature control function, the temperature rise inside the container is <5℃ @1C, guaranteeing a 15-year service life. | Inside the container, heat dissipation is centralized through 1-2 air conditioners, and the difference in temperature rise can be up to 10℃, which affects the life of the battery pack. |
| Mixed use of old and new batteries | It supports the mixed use of old and new batteries, avoiding the barrel effect, maximizing charging and discharging of the energy storage system, and enabling staged replenishment mode. | It does not support the direct mixing of old and new batteries; the energy storage system can not maximize the charge and discharge; the difference between the internal resistance of the old and new batteries is caused by the circulation, bringing heat and accelerating the aging of the new battery. |
| Minimal operation and maintenance | Automatic optimization of charging and discharging of new batteries, no need to manually adjust the backup battery, station operations, and maintenance personnel to replace the battery module directly; reduce the associated operation and maintenance costs by more than 90 | Requires experts to manually go to the station to adjust the SOC of spare batteries and replace them. |
| AI internal short circuit detection | Sudden internal short-circuits can be detected by a severe short-circuit identification algorithm and derivative internal short-circuits can be detected by an A1 outlier algorithm. | Difficulty in recognizing internal short-circuit faults and the risk of fire. Ultimate safety. |
High-voltage cascaded solution: a highly efficient solution without parallel structure
The high-voltage cascaded energy storage solution uses power electronics to achieve a grid-connected voltage of 6-35kV without going through a transformer. Taking the Xinfengguang 35kV solution as an example, a single energy storage system is a 12.5MW/25MWh system, and the electrical structure of the system is similar to that of a high-voltage SVG, consisting of three phases: A, B, and C. Each phase contains 42 H-bridge power units paired with 42 battery clusters. The three phases have a total of 126 H-bridge power units and 126 battery clusters, storing a total of 25.288 MWh of electricity. Each battery cluster contains 224 cells connected in series.
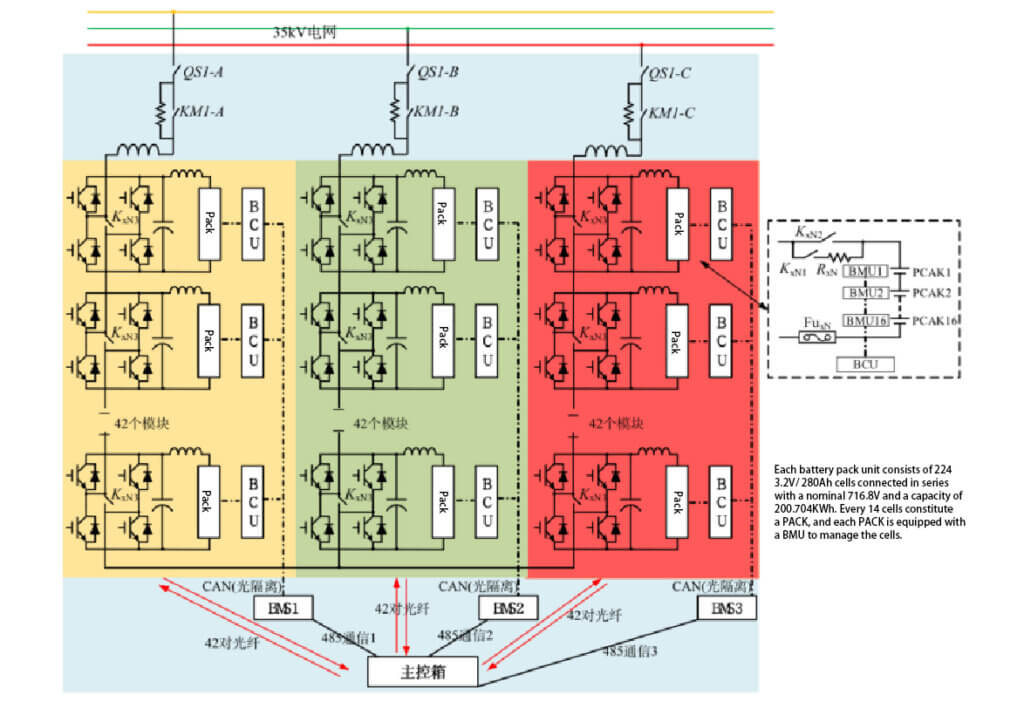
The advantages of the high-voltage cascade solution are as follows:
(1) Safety: There are no cells connected in parallel in the system, so if some batteries are damaged, the scope for replacement is narrow, the impact is small, and maintenance costs are low.
(2) Consistency: The battery packs are not directly connected but are connected after AC/DC, so all battery packs can be controlled by AC/DC for SOC balancing. Inside the battery pack are only individual cell clusters, and there is no parallel connection of cell clusters, so there is no problem with current sharing. Within the battery cluster, cell balancing control is achieved via the BMS. This solution, therefore, maximizes the use of cell capacity. Fewer cells can be installed with the same amount of grid-connected power on the AC side, reducing the initial investment.
(3) High efficiency: Since the system does not operate in parallel with the cells/battery clusters, there is no short-circuit effect, and the system life is approximately equal to the single-cell life, which maximizes the operating economy of the energy storage device. The system does not require a boost transformer, and the on-site system cycle efficiency can reach 90%.
The high-voltage cascaded solution is a new technical approach that has yet to be verified and operational.
(1) Technical aspects: Each phase of the high-voltage cascade solution is 35kv, and the electromagnetic environment is harsh, which places higher demands on BMS control. The high-voltage cascade solution is connected in parallel on the AC side, with multiple H-bridges selected for connection. ABC three-phase AC power, with various H-bridges connected in series for each phase, reduces reliability. To improve reliability, a redundant design is required. A certain H-bridge can be switched to the bypass circuit if it fails.
(2) Operation: In the 35kV energy storage system, the DC and AC sides are placed in the same location, making operation and maintenance more difficult and posing certain safety risks. The penetration rate of high-voltage cascading solutions is still relatively low, and reliability and stability need to be verified through multiple projects.
| High-voltage cascade solution | Traditional solution | |
| Maximum conversion efficiency | 98.50% | 97% |
| Power quality | THDv:<1% THDi:<3% | THDv:<3% THDi:<5% |
| Stand-alone capacity | Up to 12MW | Up to 1MW, generally 500kW |
| Response time | <20ms | Around 100ms |
| Reliability | Redundant design, fault bypass | Fail-safe shutdown |
| Battery utilization | Two-stage active balancing, high battery utilization | No active balancing, low utilization |
Distributed solution: DC isolation + centralized inverter
The distributed solution is also known as a DC-side multi-branch parallel connection. Based on the traditional centralized solution, a DC/DC converter is added at the battery cluster outlet to isolate the battery cluster. The DC/DC converter is connected to the centralized PCS DC side after collection. 2 to 4 PCS are connected in parallel to a local transformer, which is then connected to the grid after being boosted by the transformer. Adding DC/DC isolation in the system avoids DC arcing, circulating currents, and capacity losses caused by DC parallel connection, significantly improving system safety and, thus, system efficiency. However, since the system needs to go through two stages of inversion, it has a reverse effect on system efficiency.
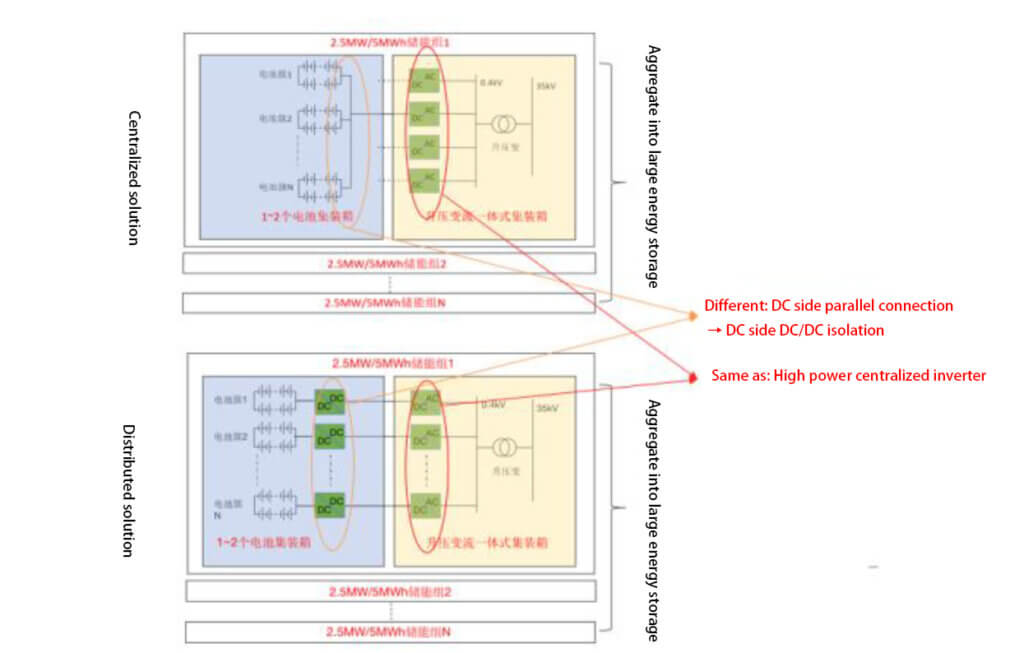
Summary: Comparison of technical routes
| Centralized | Distributed | Intelligent string | High-voltage cascading | Distributed | |
| Power conversion | Level 1 | primary | Two-stage | 6kv/10kv/35kv AC | two-level |
| Series-parallel connection | DC parallel | AC side parallel connection | DC side parallel connection | direct hanging | DC side parallel connection |
| DC isolation | No | with | with | series connection only, no parallel connection | with |
| Control accuracy | Multiple battery clusters | single battery clusters | single battery cluster | / | single cell clusters |
| Safety | With long-term operation, there is a significant inconsistency between the centralized cells and battery clusters | avoids parallel circulating currents, capacity loss, and the risk of DC arcing caused by parallel connection on the DC side | is more compatible with batteries and can achieve one package, one optimization, and one cluster, one management. | single battery cluster system, no parallel connection, no current sharing problem, better battery consistency | avoids DC arcing, circulating currents, and capacity loss |
| Efficiency | 87.80% | 90% |








2 thoughts on “Technological trends in the integration of large-scale energy storage plants”
you’re really a good webmaster. The web site loading speed is incredible. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a magnificent job on this topic!
I truly enjoy reading on this internet site, it holds wonderful blog posts.