The Truth About Low Charge in Lithium-Ion Batteries | KHZH
Part 1: Understanding Low Battery in Lithium-Ion Batteries
What is a Low Battery State for Lithium-Ion Batteries?
A low battery state for lithium-ion batteries refers to the critical stage when the battery’s charge level has significantly decreased and is nearing depletion. Unlike traditional battery types like alkaline or NiCad, lithium-ion batteries exhibit distinct behavior when their charge diminishes. This includes a gradual decline in voltage output, which subsequently impacts overall performance.
Effects of Low Battery Levels in Lithium-Ion Batteries
Low battery levels in lithium-ion batteries lead to several consequences. The most immediate effect is a voltage drop, resulting in reduced voltage output. This decline can cause electronic devices to run slower, experience lag, or even shut down entirely.
Additionally, low battery can lead to capacity degradation. As lithium-ion batteries deplete their charge, their ability to retain charge diminishes, requiring more frequent charging. This impacts user convenience and device usability.
Prolonged exposure to a low state of charge can also damage battery cells. Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to over-discharge, which occurs when the battery is depleted beyond its recommended limit. Over-discharge can cause irreversible damage, leading to reduced efficiency, shortened lifespan, and potential safety hazards like swelling or overheating.
Part 2: Causes of Low Battery in Lithium-Ion Batteries
Factors Contributing to Battery Drain in Lithium-Ion Batteries
High Discharge Rates
High discharge rates, such as when powering energy-intensive applications, cause lithium-ion batteries to deplete more quickly. Rapid charge consumption accelerates wear and tear on the battery, leading to a decline in overall capacity over time.
Overcharging
Overcharging occurs when a lithium-ion battery continues to receive power after reaching full capacity. This overcharging can stress the cells, resulting in performance degradation and reduced capacity. Over time, this degradation can increase the likelihood of experiencing low battery issues.
Deep Discharging
Deep discharging is depleting a lithium-ion battery to its lowest possible charge level. Unlike some other battery types, lithium-ion batteries are more vulnerable to deep discharging, which can cause irreversible cell damage. This results in reduced efficiency, diminished capacity, and more frequent instances of low battery.
Environmental Factors Influencing Lithium-Ion Battery Performance
Extreme Temperatures
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, significantly impact lithium-ion battery performance. High temperatures can accelerate internal chemical reactions, leading to faster degradation and capacity loss. Conversely, low temperatures can slow down these chemical reactions, temporarily affecting performance. To maintain battery health, it’s crucial to avoid exposing lithium-ion batteries to extreme temperatures and store them in a moderate environment.
Humidity Levels
Humidity can also affect the performance of lithium-ion batteries. High humidity can introduce moisture into the battery, potentially causing internal damage. Maintaining proper storage conditions helps preserve the battery’s integrity and prevent performance issues.
Managing the Health and Lifespan of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are widely used in many portable devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Their reliability, high energy density, and ability to hold a charge for extended periods make them ideal for modern technology. However, like all batteries, they require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. We will now explore factors affecting lithium-ion battery health and offer tips for extending their lifespan.
Part 1: The Impact of Temperature on Battery Performance
Lithium-ion batteries are highly sensitive to temperature, and both extreme heat and extreme cold can affect their performance and lifespan.
- High temperatures can cause accelerated chemical reactions inside the battery, leading to faster degradation of internal components. Prolonged exposure to high heat can also increase the risk of thermal runaway, potentially leading to battery damage or even igniting a fire.
- Low temperatures can reduce the battery’s ability to hold a charge. Charging the battery at extremely low temperatures can cause irreversible damage.
To maintain battery health, always store and use your devices within a suitable temperature range (20°C to 25°C or 68°F to 77°F) when possible. Avoid leaving devices in hot environments, such as cars, and ensure they are not exposed to freezing conditions.
Part 2: Protecting Lithium-Ion Batteries from Moisture
Moisture can have a significant negative impact on battery performance. Excessive moisture can corrode the internal components of lithium-ion batteries, leading to malfunctions, reduced capacity, or even failure.
To minimize the risk of damage:
- Store devices in well-ventilated, dry environments.
- Use protective cases or covers to shield devices from moisture.
- Avoid leaving devices in high-humidity areas for extended periods, especially without adequate protection.
- Regularly clean your devices to remove any moisture or debris that may accumulate.
Part 3: Managing Low Battery States
Maintaining an appropriate charge level is crucial for extending the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. Here’s how to manage low power effectively:
- Use Original Chargers: Always use chargers and cables specifically designed for your device. Generic or counterfeit chargers may lack the necessary protection mechanisms, potentially causing damage.
- Avoid Overcharging: Disconnect the charger once your device reaches 100%. Leaving devices plugged in for extended periods can cause battery wear, shortening its lifespan.
- Charge at Appropriate Temperatures: Charge your devices within a moderate temperature range to ensure efficient charging. Charging in excessively hot or cold environments can impair battery performance.
- Monitor the Charging Process: Keep an eye on the charging status to ensure it is proceeding normally. If the device shows signs of overheating or exhibits unusual behavior, disconnect it immediately.
Part 4: Long-Term Battery Care
Proper long-term maintenance is essential for maintaining the health of lithium-ion batteries:
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Lithium-ion batteries perform best when operated at temperatures between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F). Never expose devices to direct sunlight, high heat, or freezing conditions.
- Partial Charging is Okay: Unlike older battery technologies, lithium-ion batteries do not suffer from the memory effect. You can frequently charge your devices at any time, even before the battery is fully depleted.
- Use Original Chargers: Always use the charger and cable recommended by the manufacturer. This ensures efficient and safe charging, and helps prevent battery damage.
- Storage Tips: If you need to store a device or battery, keep it at around 50% charge and store it in a cool, dry place. Avoid storing batteries fully charged or completely depleted, as this can negatively impact their lifespan.
- Regular Use: Lithium-ion batteries benefit from regular use. If you have spare batteries, rotate them periodically to maintain their capacity.
Part 5: Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know when my lithium battery is low?
You can check the battery status on your device’s display or use a battery monitoring app if one is available. Devices typically provide low-battery alerts when the charge falls below the 20%-30% mark.
What is considered a low battery level for lithium-ion batteries?
While the exact threshold can vary, a lithium-ion battery is generally considered low when it falls below 20% to 30% charge. Promptly charging the battery before it gets too low will help prolong its lifespan.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your lithium-ion batteries remain in optimal condition, providing reliable performance over time.
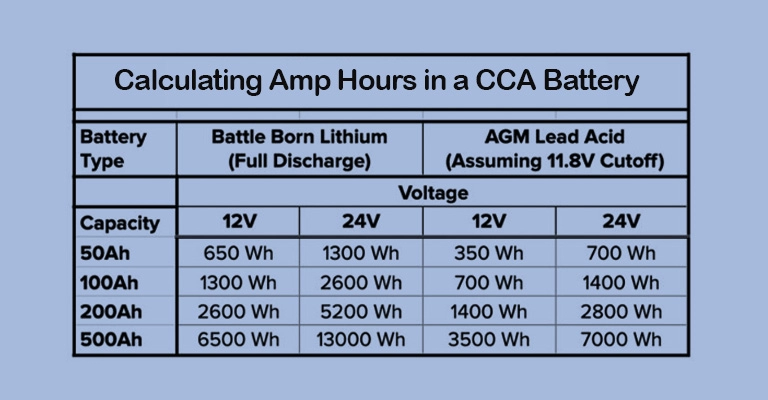
Low Voltage of 3.7V Lithium Battery
A 3.7V lithium battery is considered to have reached a low voltage level when its voltage drops below 3.2V to 3.4V. At this point, the battery is nearing its depletion point and should be charged as soon as possible to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
What is the Low Voltage for an 18650 Battery?
An 18650 lithium-ion battery is considered to have a low charge when its voltage drops below 3.2V to 3.4V. This indicates that the charge is significantly depleted, and it is recommended to charge it to ensure proper operation and battery health.
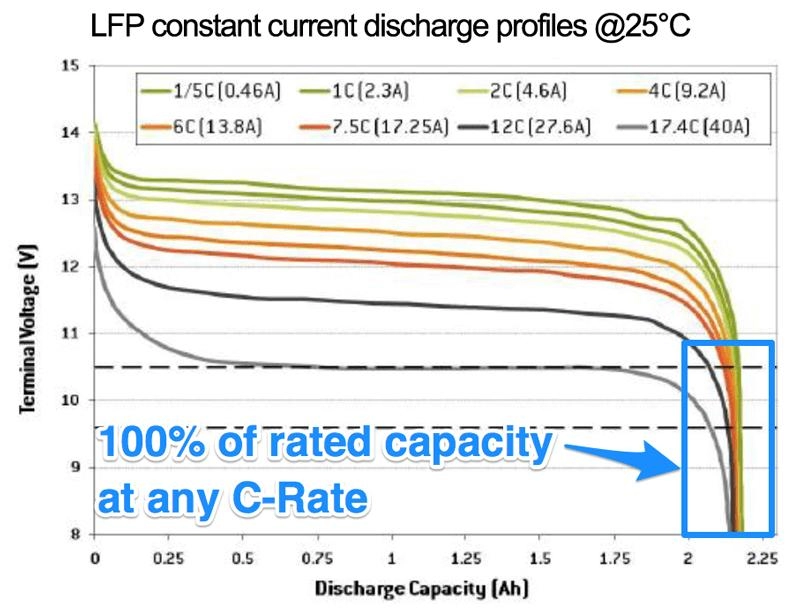
At What Voltage is a Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Dead?
A LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery is considered fully discharged when its voltage drops below 2.5V to 2.8V per cell. Discharging below this threshold can lead to irreversible damage, shortening its lifespan and affecting future performance.
Related Articles
The Best Way to Store Batteries
Learn the best practices for storing batteries to maximize their lifespan and ensure safety. Learn expert tips to keep them in good condition and prevent damage.
LiPo Battery Storage Voltage Explained Simply
Proper LiPo battery storage voltage is critical for extending battery life. Maintaining a voltage between 3.7V and 3.85V per cell helps preserve battery health and minimize long-term wear.
Decoding Lithium Battery Cost: Factors Influencing Pricing
Explore the key factors influencing lithium battery pricing. This in-depth analysis covers market trends, cost components, and the future outlook for lithium battery costs.
Liquid Metal Batteries vs. Lithium Batteries: A Comparative Analysis
Compare liquid metal batteries vs. lithium batteries – a comparative analysis of characteristics, applications, advantages, disadvantages, costs, and energy storage potential.
Understanding LiPo Batteries: Capacity, Lifespan, and More
A comprehensive look at LiPo batteries, including capacity, energy density, cycle life, and tips for optimizing performance while avoiding common pitfalls.
KHZH – Your Trusted Source for Battery Knowledge