In today’s world, batteries have become an indispensable part of daily life, powering everything from household appliances to electric vehicles. Among the various types of batteries, standard batteries are particularly important due to their versatility and widespread availability. Understanding the different types, sizes, and capabilities of standard batteries can help you make informed decisions and choose the most suitable battery for your needs. This guide will explore everything you need to know about standard batteries, including their types, uses, maintenance, and safety precautions.
Part 1: What is a Standard Battery?

A standard battery is a portable energy storage device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions. These batteries are designed to provide reliable power for a wide range of applications, making them an integral part of everyday consumer electronics and specialized equipment. The term “standard battery” typically refers to common battery sizes and types that can power many different devices.
Part 2: Types of Standard Batteries
Non-Rechargeable Batteries
Non-rechargeable batteries are designed for single use and must be replaced once depleted. They are commonly used in low-power devices. Popular types of non-rechargeable batteries include:
- Alkaline Batteries (e.g., AA (LR6) (pronounced: Ā Ā), AAA (LR03) (pronounced: Ā Ā Ā), C (LR14) (pronounced: Sī), D (LR20) (pronounced: Dī)): Commonly found in household items like remote controls and flashlights, alkaline batteries are known for their long shelf life and reliability.
- Lithium Batteries (e.g., CR2032, CR123A): Offering higher energy density, these batteries power cameras, watches, and other high-drain devices.
- Silver Oxide Batteries (e.g., SR626, SR626W): Known for their stable voltage and high capacity, silver oxide batteries are commonly used in small devices like watches and hearing aids.
Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable batteries can be used multiple times, making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly in the long run. These batteries are suitable for high-drain devices and applications. Common types include:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries (e.g., 18650, 21700): Widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are prized for their high energy density and lightweight design.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries (e.g., AA, AAA): These rechargeable batteries are often used in household devices like digital cameras and cordless phones.
- Lead-Acid Batteries (e.g., car batteries, deep-cycle batteries): Known for their durability, lead-acid batteries are commonly used in vehicles and backup power systems due to their high current output.
Part 3: Standard Battery Sizes and Models
Standard batteries come in various sizes, each with specific models that indicate their dimensions and chemical properties. Some of the most commonly used sizes include:
- AA (LR6): One of the most popular battery sizes, found in devices ranging from toys to remote controls.
- AAA (LR03): Smaller than AA batteries, AAA batteries are commonly used in small devices like TV remotes and flashlights.
- C (LR14): These batteries are used in larger devices like portable radios and toys.
- D (LR20): D batteries are used in high-drain devices like large flashlights and toys.
- 9V (6F22): Commonly used in smoke detectors and guitar effects pedals, 9V batteries provide higher voltage in a compact form.
- CR2032: A commonly used lithium coin cell battery, ideal for powering watches, calculators, and other small electronic devices.
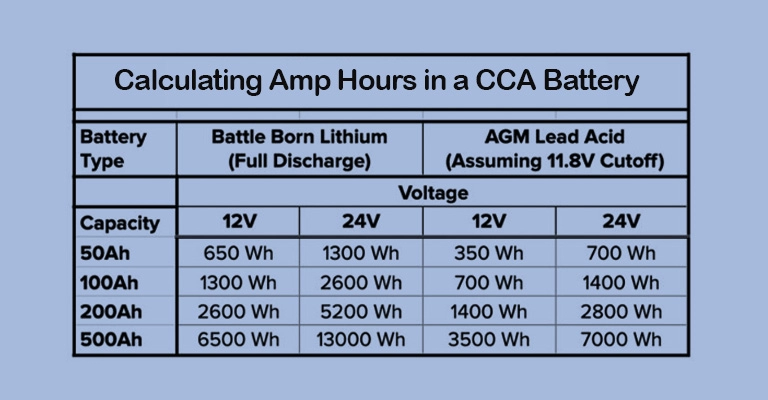
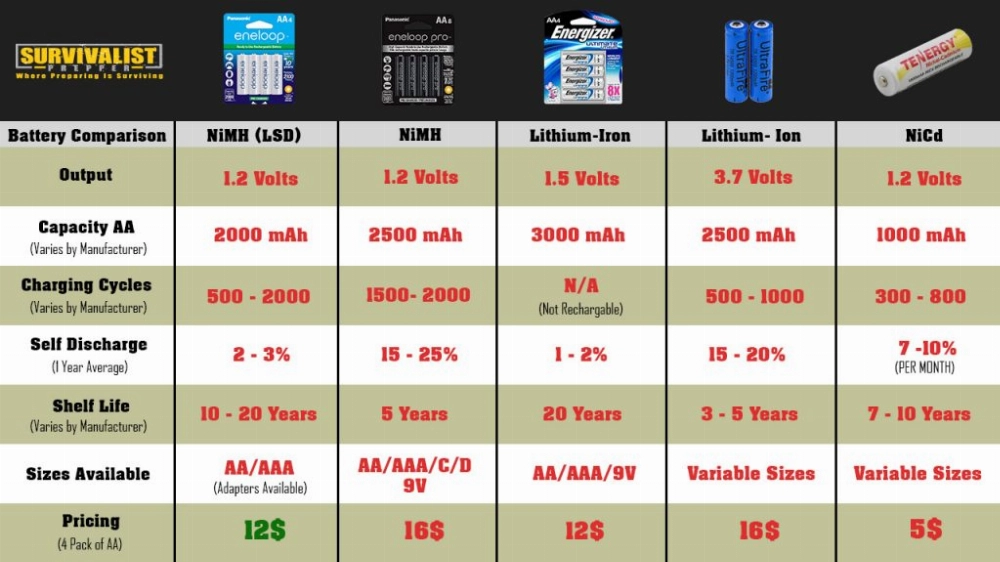
Part 4: Battery Capacity and Voltage Explained
Battery capacity refers to the amount of energy a battery can store, typically measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or ampere-hours (Ah). A higher capacity means the battery can power a device for a longer period. Voltage, measured in volts (V), represents the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. Different battery chemistries have different nominal voltages:
- Alkaline Batteries: 1.5V per cell
- Lithium Batteries: 3V per cell
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: 1.2V per cell
Understanding these concepts can help you select the right battery based on your device’s power requirements and desired battery life.
Conclusion
Batteries are essential to the functioning of our modern world, from powering everyday devices to supporting key technologies like electric vehicles. By understanding the different types, sizes, and capabilities of standard batteries, you can make more informed choices for your various devices. Whether you’re looking for a reliable alkaline battery or a high-capacity lithium-ion solution, selecting the right standard battery will ensure optimal device performance. For more information, refer to our guide on the Top 10 Best 24V Lithium Batteries 2025.
Part 5: Common Uses of Standard Batteries
Standard batteries are widely used in various applications, such as:
- Consumer Electronics: Many everyday devices, including remote controls, cameras, and portable speakers, rely on standard batteries for power.
- Toys: Many battery-powered toys rely on standard batteries, making them convenient to replace and maintain.
- Medical Devices: Important medical devices like glucose meters and portable oxygen concentrators often use standard batteries to ensure reliability.
- Automotive Applications: Lead-acid batteries are crucial for starting vehicles and powering automotive electrical systems.
- Emergency Equipment: Devices like smoke detectors and flashlights commonly use standard batteries to ensure they function in emergencies.
Part 6: Understanding Battery Ratings
When purchasing batteries, you may encounter ratings that indicate their performance. Important ratings include:
- Capacity Rating (mAh): This refers to the amount of electrical charge a battery can store. A higher mAh rating generally means longer usage time.
- Discharge Rate: This indicates how quickly a battery can release its electrical energy. Devices with high power demands require batteries with higher discharge rates.
- Cycle Life: This represents the number of charge and discharge cycles a rechargeable battery can undergo before its capacity significantly decreases.
Part 7: Battery Care and Safety: Practical Tips and Common Misconceptions
Battery Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount when handling standard batteries. Keep these safety tips in mind:
- Avoid Mixing Batteries: Mixing different types, brands, or chemistries of batteries can lead to leakage or rupture. Always use the same type of batteries in a device.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of used batteries in accordance with local regulations. Many regions offer recycling programs to prevent environmental damage.
- Storage Conditions: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Extreme temperatures can affect their performance and safety.
- Check Expiry Dates: Check the expiry dates of batteries before using them. Expired batteries may leak or fail to function properly.
Battery Maintenance Tips
To prolong battery life and ensure optimal performance, follow these maintenance guidelines:
- Remove Batteries When Not in Use: If storing a device for an extended period, remove the batteries to prevent leakage and potential device damage.
- Keep Contacts Clean: Regularly clean battery contacts to ensure a good connection and prevent corrosion.
- Use the Correct Charger: Always use the recommended charger for rechargeable batteries to avoid damage and ensure efficient charging.
Common Misconceptions About Standard Batteries
Debunking these misconceptions can help you better understand battery care:
- Misconception 1: All Batteries Are the Same
Batteries vary in chemistry, size, and capacity. Using the correct type is essential for a device’s performance. - Misconception 2: You Can Recharge Any Battery
Only rechargeable batteries can be recharged. Attempting to recharge non-rechargeable batteries can be dangerous. - Misconception 3: Batteries Lose Power Over Time
While batteries may lose power during storage, proper storage can minimize this loss and preserve performance.
Part 8: Frequently Asked Questions
How long do standard batteries last?
On average, the lifespan of standard batteries varies depending on their type, usage, and storage conditions. Alkaline batteries typically last for 3-5 years, while rechargeable batteries last for 2-3 years, depending on usage.
Can I use rechargeable batteries in devices designed for alkaline batteries?
Yes, rechargeable batteries can be used in devices designed for alkaline batteries. However, keep in mind that rechargeable batteries have a lower nominal voltage (1.2V compared to 1.5V for alkaline batteries), which may affect the performance of some devices.
How do I know when to replace batteries?
To determine when to replace batteries, monitor the device’s performance. If the device begins to lose power rapidly or ceases to function, the batteries need replacing.
Signs Your Battery Needs Replacing
If you notice your device dimming, running slower, or not functioning correctly, it may be time to replace the battery. These signs often indicate that the battery is losing charge or becoming less efficient. Checking and replacing the battery promptly can restore optimal performance.
Are There Eco-Friendly Battery Options?
Yes, there are eco-friendly alternatives to standard batteries. Manufacturers now offer rechargeable NiMH batteries for multiple uses, reducing waste. Additionally, many regions have battery recycling programs to ensure proper disposal, minimizing environmental impact.
What Should I Do If a Battery Leaks?
If you discover a battery leaking, handle with care. Wear gloves for protection and clean the area with a damp cloth. Dispose of the leaking battery according to local regulations and avoid direct contact with the leakage to prevent harmful reactions.
Related Articles:
- Best Ways to Store Batteries –
Learn the best practices for storing batteries to extend their lifespan and ensure safety. Learn helpful tips to keep them organized and prevent damage. - Lipo Battery Storage Voltage Explained –
Understanding the optimal storage voltage for Lipo batteries (3.7V–3.85V per cell) is crucial for maintaining battery health and minimizing wear during storage. - Decoding Lithium Battery Costs: What Influences Pricing? –
Explore how the cost of lithium batteries is influenced by various factors, trends, and what the future holds. - Liquid Metal Battery vs Lithium-Ion –
Compare the characteristics, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of liquid metal batteries versus lithium-ion batteries. Gain insights into their future prospects and cost considerations. - Understanding Lipo Battery: Capacity, Lifespan & More –
Delve into the specifications of Lipo batteries, including capacity, energy density, and cycle life. Learn how to optimize performance and avoid common pitfalls.
Written by KHZH – Your trusted source for battery industry insights and advice.