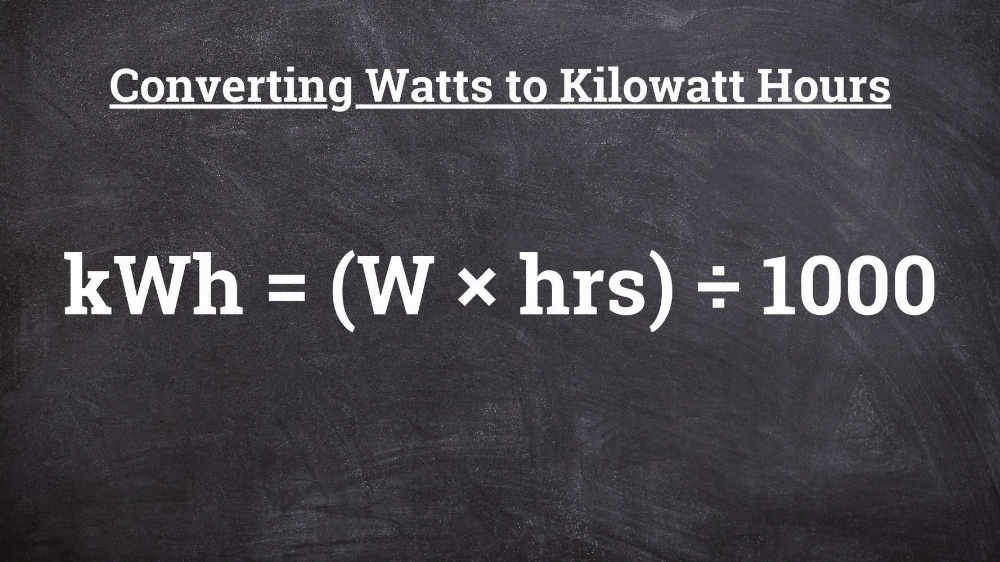Battery Selection: Understanding the Difference Between Watts and Watt-Hours
When choosing a battery that meets your needs, understanding the difference between watts (W) and watt-hours (Wh) is crucial. Watts (W) measure the rate of power usage, while watt-hours (Wh) represent energy capacity, respectively. This guide will break down their definitions, differences, and practical applications, and provide a clear comparison table and step-by-step calculations to help you gain a deeper understanding of battery performance metrics.
Part 1: What are Watt-Hours in a Battery?
A battery’s watt-hours (Wh) measure the total energy it can store. It tells you how much power the battery can provide over a specific period. For example, if a battery has a capacity of 100 watt-hours, it can deliver 100 watts of power for one hour, 50 watts of power for two hours, and so on.
Watt-hour ratings are essential for understanding battery life: how long a device can run before needing a recharge. It can help you choose the right battery for various applications, such as smartphones, laptops, or electric vehicles, ensuring the device functions properly for the desired runtime.
Part 2: What are Watts in a Battery?
A battery’s wattage refers to the rate at which the battery provides power. It measures the rate at which energy is transferred. For example, if a battery provides 50 watts of power, it can deliver 50 joules of energy per second.
Understanding watts is crucial because it shows how quickly a battery can power a device. Batteries with higher wattages can either charge devices faster or support devices with higher power demands. This metric is key to ensuring compatibility and optimal performance when selecting a battery for a specific purpose.
Part 3: What is the Difference Between Watts and Watt-Hours in a Battery?
- Watts measure instantaneous power consumption or the rate of power generation.
- Watt-hours quantify the total energy consumed or stored over a period of time.
In short, watts indicate the speed at which energy is used or generated.
# Battery Capacity: Understanding Watt-Hours and Wattage Calculations
Part 1: How to Calculate Watt-Hours
To understand a battery’s energy storage capacity, it’s crucial to calculate its watt-hours. Watt-hours (Wh) represent the total amount of energy a battery can store and provide over time. It’s an important metric for determining how long a device can run on battery power.
Watt-Hour Conversion Formula
If you know the battery’s capacity in Amp-hours (Ah), you can easily calculate the watt-hours (Wh) by multiplying the voltage (V) by the capacity (Ah). The formula is as follows:
Watt-hours (Wh) = Voltage (V) × Capacity (Ah)
For example:
- A 12-volt battery with a capacity of 5 Amp-hours:
Watt-hours (Wh) = 12V × 5Ah = 60 Wh
Important Considerations:
- Ensure that the voltage and capacity are in consistent units (e.g., volts and amp-hours).
- Nominal voltage can vary depending on the battery type (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion).
- A battery’s capacity may decrease with use over time, so the calculated watt-hours may not reflect its current performance.
Pro Tip:
For easy comparison, especially when comparing batteries with different voltages, it’s recommended to convert the capacity to watt-hours. For example:
- 12V 10Ah battery = 120Wh
- 24V 5Ah battery = 120Wh
Even though these batteries have different voltages, they have the same energy capacity.
Part 2: Wattage and Watt-Hours in Battery Applications
Battery Selection
Understanding wattage and watt-hours is essential when selecting a battery for a specific application. Knowing the watt-hours helps ensure the battery has sufficient capacity to power the device for the required duration without frequent recharging.
How many watt-hours are in an AA battery?
AA batteries typically contain between 5 and 15 watt-hours of energy, depending on the type and brand. The amount of energy you can get from the battery will vary depending on how it’s used, even when used in a 12-volt device, and different brands offer different energy densities.
How many watt-hours are in a cell phone battery?
The watt-hour capacity of cell phone batteries can also vary greatly. However, most standard smartphone batteries contain approximately 5 to 15 watt-hours of energy, providing sufficient power for daily use and multiple charging cycles.