Licoo2 batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery that are well-regarded for their impressive energy density and reliable performance. This guide delves into the definition, working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and various uses of Licoo2 batteries in everyday life. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply curious about battery technology, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of Licoo2 batteries.
What is an Licoo2 Battery?
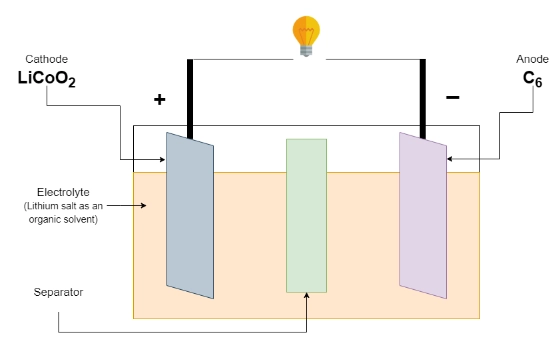
An Licoo2 battery is a rechargeable lithium-ion battery that uses lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) as its cathode material. Their high energy density makes them highly efficient and commonly used in applications requiring compact and powerful energy storage, including electric vehicles and portable electronics. Licoo2 batteries are valued for their ability to maintain a consistent voltage and they offer a relatively long cycle life compared to other types of batteries.
How Does an Licoo2 Battery Work?
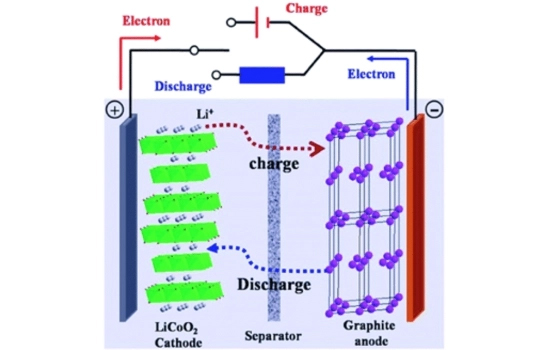
The functionality of an Licoo2 battery involves several key components that contribute to its exceptional energy density and long cycle life. During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, making them well-suited for high-energy devices like electric vehicles and mobile electronics.
- Anode: Typically made of graphite, the anode stores lithium ions during charging.
- Cathode: Composed of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), the cathode releases lithium ions during discharge.
- Electrolyte: A lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode.
When an Licoo2 battery is charged, lithium ions flow from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte. During discharge, this process reverses, with the ions returning to the cathode and producing electrical energy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Licoo2 Batteries
Licoo2 batteries offer several compelling advantages, particularly in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles and smartphones. However, it’s also important to consider their cost, thermal stability, and environmental impact when choosing the best battery technology.
Advantages
- High Energy Density: Licoo2 batteries have a high energy density, enabling devices to operate longer on a single charge. This makes them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- Stable Voltage Output: These batteries maintain a consistent voltage throughout their discharge cycle, ensuring reliable performance, which is crucial for sensitive electronic devices.
- Long Cycle Life: If properly maintained, Licoo2 batteries can last for hundreds of charge and discharge cycles, providing better cost-effectiveness.
- Lightweight: The compact design of Licoo2 batteries contributes to their lightweight nature, which is particularly beneficial for mobile devices and applications where weight is a critical factor.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Due to the cost of cobalt, Licoo2 batteries can be expensive to produce, and cobalt mining conditions are often harsh, making these batteries pricier than other alternatives.
- Thermal Safety: If not properly managed, Licoo2 batteries can overheat and experience thermal runaway. Therefore, advanced battery management systems are necessary.
- Environmental Concerns: The extraction and disposal of cobalt raise significant environmental and ethical issues. As demand for batteries grows, sourcing sustainable materials becomes increasingly important.
Applications of Licoo2 Batteries
Licoo2 batteries are widely used in high-demand applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops, and even medical devices. Their high energy density and long cycle life make them an ideal choice for applications where reliability and performance are paramount. For more on high-performance battery applications, check out our guide on Mastering RV Fridge on Battery Power While Driving.
- Consumer Electronics: Laptops, smartphones, and tablets commonly rely on Licoo2 batteries for their impressive energy capacity and long lifespan.
LiCoO2 Batteries: Applications, Maintenance, and Comparison
Part 5: LiCoO2 Battery Maintenance
To maximize the lifespan and performance of LiCoO2 batteries, it is crucial to follow proper maintenance guidelines.
1. Avoid Overcharging:
Use a compatible charger and disconnect it promptly once fully charged.
2. Proper Storage:
For extended periods of non-use, store the battery in a cool, dry place, maintaining a charge level between 40% and 60% for optimal preservation.
3. Monitor Temperature:
Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures, as overheating can cause damage and shorten its lifespan.
4. Frequent Use:
Use the battery regularly and avoid deep discharges to prevent severely impacting its capacity.
Part 6: Comparison of LiCoO2 Batteries with Other Lithium-Ion Batteries
When comparing LiCoO2 batteries with other lithium-ion battery materials, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4), factors like energy density, cycle life, and cost-effectiveness come into play. LiCoO2 batteries are favored for their high energy density in applications where compactness and lightweight design are essential, such as in electric vehicles (EVs) and portable electronics.
Key Comparisons:
- Energy Density: LiCoO2 batteries have a higher energy density, typically ranging from 150 to 200 Wh/kg. In comparison, LiFePO4 batteries have a lower energy density (90 to 120 Wh/kg), making LiCoO2 batteries more suitable for lightweight, high-performance applications where maximizing power in a small volume is critical.
- Cycle Life: LiCoO2 batteries typically have a cycle life of 500-1500 cycles, depending on usage and maintenance. In contrast, LiFePO4 batteries can last for 2,000 cycles or more, making them a better choice when longevity is a priority.
- Thermal Stability: LiCoO2 batteries have only moderate thermal stability and may pose a risk of overheating. On the other hand, LiFePO4 batteries are known for their high thermal stability, which makes them safer to use in extreme conditions.
- Cost: LiCoO2 batteries can be relatively expensive due to the high cost of cobalt. In comparison, LiFePO4 batteries are often more affordable, making them a cost-effective choice in some applications.
- Environmental Impact: The mining of cobalt required for LiCoO2 batteries raises significant environmental and ethical concerns. On the other hand, LiFePO4 batteries use iron, which is a more abundant material and has a lower environmental impact.
Comparison of LiCoO2 with Other Lithium-Ion Battery Materials:
| Characteristic | LiCoO2 Battery | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150-200 Wh/kg | 90-120 Wh/kg | 100-150 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 500-1,500 Cycles | Up to 2,000 Cycles | 500-1,000 Cycles |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Cost | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Significant Concerns | Lower Impact | Moderate |